Although a car is a complex device consisting of tens of thousands of parts, we consider the engine to be its "heart". After all, it was the invention of the internal combustion engine that started the history of motoring. Today, most "tin pets" are powered by a gasoline or diesel engine, but there are other solutions…
The engine is the source of power that drives the car and gives it character. According to the engine, we can find out how fast a car is, how much it consumes and where it has a place on the price scale. Unfortunately, the engine is also the most expensive part of the vehicle that we can destroy.
Before we get to work, let's clarify what "internal combustion" is. Thermal motors (propulsion machines that use fuel combustion to generate energy) can have a separate combustion point (eg combustion chamber for steam locomotives) or integrated into the construction of the engine itself, which is the case with propulsion machines described here, which are called engines with internal combustion.
Most of today's cars are powered by internal combustion engines. The energy required to start the vehicle in these engines is obtained by burning a mixture of fuel (petrol, diesel, alcohol, gas, etc.) and air in the cylinders. The air needed to burn the fuel is introduced from the atmosphere into the cylinder through the intake ducts, and the fuel, placed in the tank, is supplied by a pump that delivers it to the injection system or, in older cars, to the carburetor.
The mixture of fuel and air is then compressed by the piston, which is ignited by the spark plug in the case of a petrol (Otto) engine, while in the case of a gas oil engine (Diesel) the ignition of the fuel is enabled by the high temperature of the compressed air. When the mixture is burned, the resulting gases are discharged through the exhaust system.
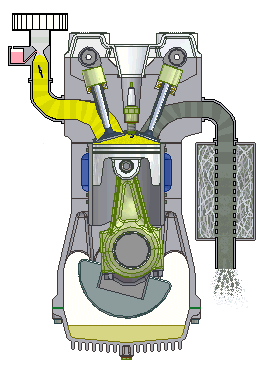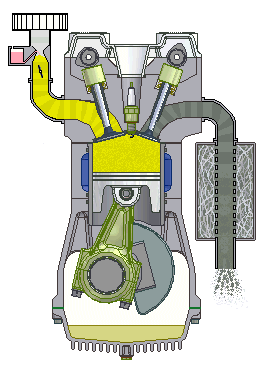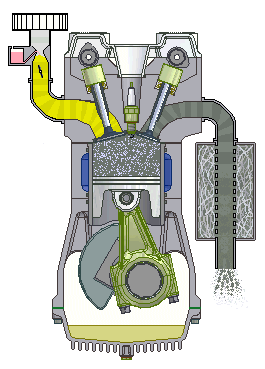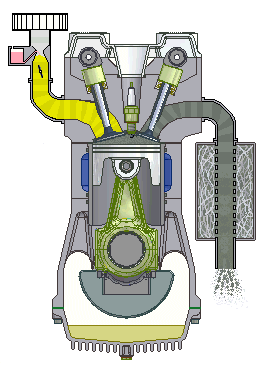
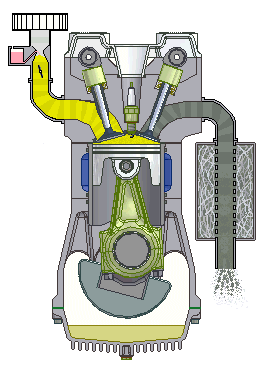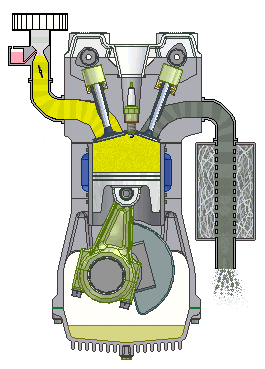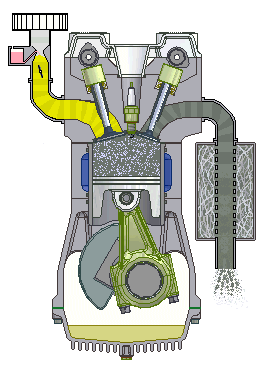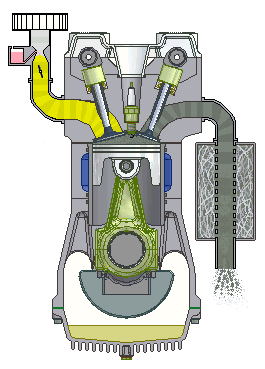
If we talk about cars, we will most often hear about the term four-stroke (4-stroke) engine. These are propulsion machines that perform the above in four phases, which we call clocks. Individually, the working phases of a four-stroke engine are called: intake, compression, expansion and exhaust stroke.
Four-stroke internal combustion engine
1st stroke - Intake: the intake valve is open, the exhaust is closed; 2nd stroke - Compression: both valves are closed and the piston compresses the mixture; 3rd bar - Expansion: the spark of the spark plug ignites the mixture and the gases spread pushing the piston; 4th stroke - Exhaust: The exhaust valve is open, the intake valve is closed.
The difference between the performance of a four-stroke Otto engine and a four-stroke Diesel engine is that in the second the third stroke, expansion, occurs as a consequence of self-ignition of fuel (gas oil) and air caused by high temperature mixture under pressure. So Diesel engines do not have a spark plug (central element at the top of the cylinder).

We said that it is necessary to mix air and fuel for combustion. If we take into account that the most favorable measure of fuel and air for complete combustion is constant (14.7: 1 in favor of air in gasoline engines - known in thermodynamics as adiabatic constant), we see how to increase the energy obtained (and thus engine power). it is simply necessary to burn more mixture. Therefore, larger displacement engines typically develop more power because they fit more mixture into the cylinder.
The piston (which compresses the mixture) moves between two positions in the work: the lower and upper dead (end) points, crossing the path we call the piston stroke. If we take into account its diameter (pistons are usually round in cross section), it is possible to represent the volume of the cylinder as the space between these two end positions of the piston (exception in this theory are pistons that do not have a flat forehead, ie upper surface). Thus, the volume of an engine can be represented as the sum of the volumes of all cylinders. Engine capacity is most often expressed in liters (for commercial purposes or as a model designation) and in cubic centimeters (eg in technical data, according to the SI system).

The Imperial system of measures uses the unit cubic inch, abbreviated cu-in. The cubic inch is 16.387064 cubic centimeters. Thus, volume (cm3) x 0.061024 = volume (cu-in).
The degree of the largest volume of the cylinder (when the piston is in the lower dead center - DMT) and the space in which the mixture is compressed by the arrival of the piston in the upper dead center (GMT) is called the degree of compression. The power of the engine significantly depends on the degree of compression, and as a rule, with its increase (up to a certain limit), it increases. Due to the need for high-temperature compressed fuel-air mixture to cause its self-ignition, Diesel engines generally have a higher degree of compression than gasoline ones.


The consequence of burning the mixture of fuel and air is an increase in the volume of gases inside the cylinder. This expansion drives the piston downwards (more precisely, towards the DMT because the engine does not always have to be placed upright). In this way, the movement of the piston is converted into a circle, which is then passed to the transmission system and eventually leads to the wheels.
In order for the engine to be able to "breathe" properly, ie. introduce the mixture into the cylinder and expel the combustion products from it, the valves are taken care of. There are two types of valves: intake and exhaust, and the rhythm of their opening and closing determines the number of engine revolutions, which changes depending on how much the accelerator pedal is pressed. Modern engines are equipped with more valves per cylinder for better gas exchange. Thus, two intake and two exhaust valves allow a (4-cylinder) 16-valve engine to significantly "breathe", and thus achieve greater power compared to the classic (2-valve) version.






Completely super informative article. I have been a driver for many years and to tell you the truth I much prefer diesel engines for a simple reason, I like to hear when they "rumble". After many years of driving diesel, I sat in the gas station, it was not my car, I just used it to go to the store from the picnic area and the traffic light was red, when it changed to green I thought my car turned off because I can't hear that works: D I still prefer diesels hahaha