
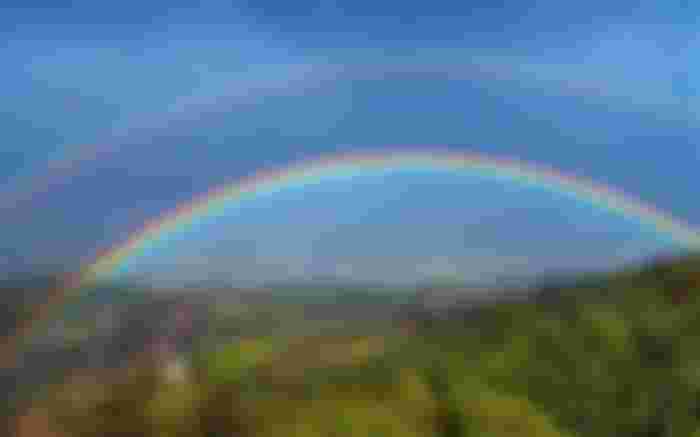
A rainbow 🌈 is a visible arc-shaped line of light caused by the reflection and reflection of sunlight on water particles in the atmosphere. Rainbows are usually seen in the sky on the opposite side of the sun after rain. The rainbow is a combination of seven colours. It is called a rainbow because it looks like a bow.

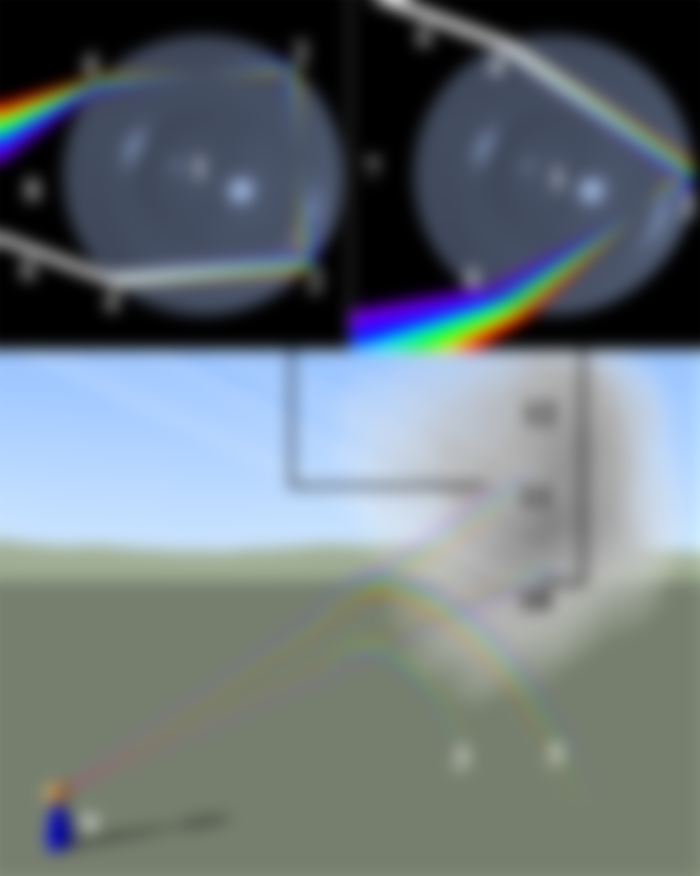
The spectrum is formed by the refraction of light as sunlight passes through raindrops or water vapor-mixed air. In this spectrum light is divided into seven colours. These seven colours are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red; In Bengali, these colours are abbreviated with their initials: Beniaasahakala ( বেনীআসহকলা) . VIBGYOR in English. Due to the different wavelengths of light in these seven colours , the amount of curvature varies. For example, the red light bends at an angle of 42. On the other hand, the purple light bends at an angle of 40. Light rays of other colours bend at different angles between 40 ° and 42. This is why the colours of the rainbow are always seen in a certain row.

A little above the initial bright rainbow is another minor rainbow that is less bright, so that the colours are in reverse order. The sky between these two bows (Alexander's dark region) is a little darker than the rest of the sky, but this difference can be overlooked if not noticed.
Thanks for Reading this 💕 💕


Great informative😍