The oceans cover as much as 71 percent of the Earth's surface. In their depths are hidden numerous plant and animal species that have adapted to life in this habitat for millions of years.

Thoughts usually draw us to the oceans and seas during the summer, while we plan where to spend our vacation, but we probably rarely ask ourselves about the importance that the oceans have for the life of the planet.
The oceans are very important for the global climate because, among other things, they absorb a significant part of the carbon dioxide emissions that come from the process of burning fossil fuels.
On the other hand, climate change has a negative impact on the oceans, and due to the increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the ocean is warming, its acidification, migration and reduction of flora and fauna, but also various other consequences.
Climate change is happening due to our uncontrolled greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere, and from the beginning of the industrial period until today, the concentration of these gases is constantly increasing. That is why, nowadays, various ways are being sought to capture and store carbon dioxide, and one of them, which nature itself has offered us, are the oceans.
Nowadays, when the consequences of climate change are visible on a daily basis, the oceans must be "honored" because they have played a significant role in making this picture milder. In fact, from the beginning of the industrial revolution until today, the oceans have absorbed about 30 percent of our carbon dioxide emissions. However, as time goes on, they "absorb" increasing amounts of CO2 and become more saturated, so their absorption power is likely to be reduced.
On the other hand, when the oceans absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it dissolves in them and continues to exist in the form of hydrocarbonic acid. The higher the amount of carbon dioxide the ocean absorbs, the higher the amount of this acid will be, and this leads to acidification, ie an increase in the acidity of the ocean, which can pose a significant risk to the survival of the living world in them.
Also, a part of carbon is bound through the process of photosynthesis in phytoplankton, microscopic algae that form the basis of ocean biodiversity. Although the field of studying the impact of climate change on phytoplankton is still relatively open, most research shows that in the future warmer climate, their number will be reduced, which would further reduce the absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Thus, the oceans have a very large impact on the climate and mitigation of climate change by "capturing" a part of the carbon dioxide that we emit and slowly pulling it into its depths. But isn't that the only way the oceans affect the climate on our planet?
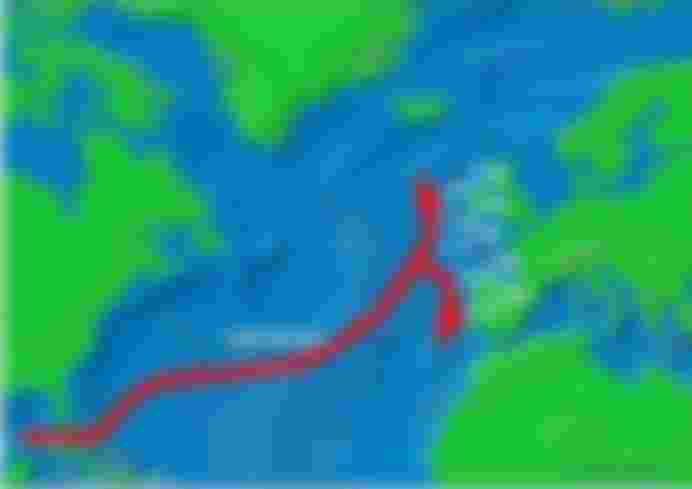
Probably the most famous phenomena of the climate system, El Niño and the Gulf Stream, represent the direct influence of the ocean, especially when we look at the climatic conditions in certain parts of the planet. In fact, the influences of these two phenomena can be felt in different places in the world, which reflects their significance.

The Gulf Stream is a warm sea current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and then flows all the way to Europe. Its influence is reflected in the fact that it causes mild winters in northern Europe, and if this warm current did not exist, certain parts of our continent would probably have a much lower temperature.
In addition to the Gulf Stream, El Niño also has a significant influence, which represents a warm phase of oscillation in the characteristics of the ocean and the atmosphere of the tropical part of the Pacific. Its power can be felt by the entire planet, especially the tropical zone, through the extreme weather conditions it causes.

When we talk about climate change, our first association is probably an increase in temperature. It occurs because greenhouse gases retain additional heat in the climate system, and the role of man can not be neglected.
However, as much as 90 percent of this extra heat goes to the oceans, so they have been slowly warming up for decades. Due to that warming of the ocean, the flora and fauna are endangered, and there are other negative consequences.
In addition to the already mentioned acidification, another big problem that is aided by climate change is deoxygenation, ie loss of oxygen. The large amount of oxygen we breathe every day came from the ocean. However, due to the warming of the oceans and the overpopulation of algae, the oceans produce less and less oxygen.
The consequences of climate change, which we can witness more and more often, are the increased intensity of tropical storms, the strength of which is directly related to the water temperature of the oceans above which they move, as well as elevated sea levels.
The average ocean level today is about 20 cm higher. And although this does not seem significant at first glance, precisely in situations when powerful hurricanes approach the land, sea water, which invades in large waves, can penetrate up to several kilometers deeper into the land, which would not happen if this "small" increase it was not. Coastal floods caused in this way often bring with them great material damage, but also the loss of human lives. A well-remembered example of this devastating combination, elevated ocean levels and stronger storms, are the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina in 2005.

Due to warmer water, increased concentration of carbon dioxide and less oxygen in it, the natural habitats of many species are changing, and the conditions for their life often become extremely difficult.
Due to the rise in temperature, many species migrate to areas where they find suitable conditions for their lives. In the past, these species migrated temporarily, during certain seasons, but today it can be noticed that they stay in their new habitat.
Unfortunately, not all plants and animals are allowed to go to the ends of the ocean that suit them better. If they cannot cope with the conditions caused by climate change, many species become extinct or are extremely endangered, as exemplified by coral reefs.

Because of all the processes that take place in the oceans, they are very important for life on Earth. If the planet continues to heat up at this rate, and we do not keep the rise in global temperature below two degrees, there is a danger that many ocean species will not be able to cope with the changes. As the oceans are one of the key links for life on Earth, such changes in the processes that take place in the oceans would have a negative impact on the entire planet and life on it.



Povezava med oceani in podnebnimi spremembami je ena izmed ključnih tem razprave na konferenci Združenih narodov (ZN) o oceanih.Oceni, ki pokrivajo tri četrtine zemljine površine, imajo ključno vlogo pri svetovnem podnebnem sistemu, proizvajajo kisik in vpijajo ogljikov dioksid iz ozračja. Spremembe v podnebju, ki jih povzročajo naraščajoči nivoji toplogrednih plinov v ozračje, bodo tako pripeljale tudi do sprememb v oceanih. Slednje vključujejo naraščajočo morsko gladino in zakisljevanje oceanov, kar pa bo ogrozilo morske ekosisteme in obmorske skupnosti.