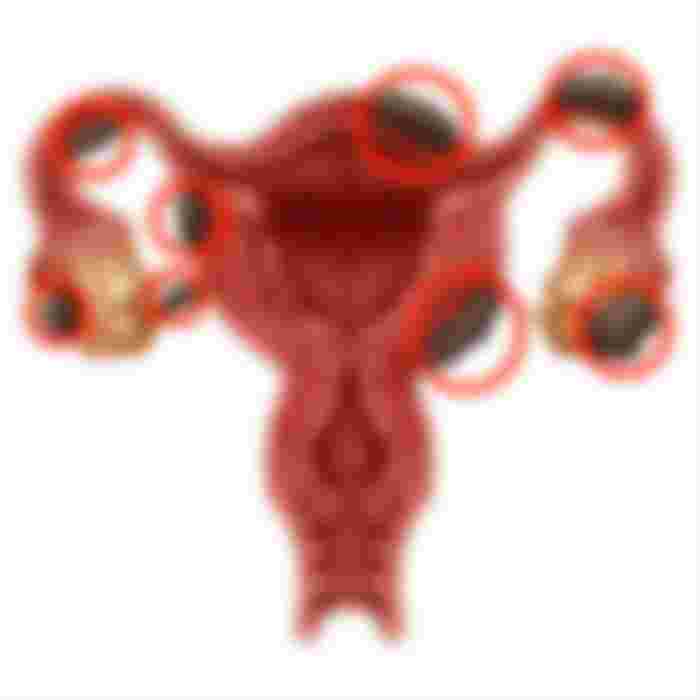
This problem, which can affect many women, is not known for sure what causes it. The endometrium is the membrane that covers the uterine cavity. Endometriosis is a displacement of the endometric tissue of the uterine cavity.
It is classified as: internal, when that tissue moves to the fallopian tubes, external, if it moves outside the uterus: to the ovaries, bladder, peritoneum, etc. Although the latter form is less common, it is nonetheless probable and worrisome.
Inexplicably, the endometrium can "go up the fallopian tubes to the ovaries and continue its course to the intestine. This disorder is more common in women in their 30s, especially if they have never had children.

In the same way that the lining tissues of the uterus are shed each month with menstruation, endometrial deposits that have developed in any other region do as well. If the bleeding that this causes occurs within the abdomen, it causes scar tissue between the endometrial reservoir and nearby tissues.
Endometriosis should not be confused with endometritis, which is nothing more than the expulsion of portions of the endometric membrane that causes dysmenorrhea and pain during menstruation.
Does infertility cause?
The healing tissues that the endometrium forms as it moves out of place can often adhere to the nearest organs, frequently interfering with their function. For example, if any of the fallopian tubes are affected by this problem, the adhesions often prevent the tube from functioning. As a result, it will be unable to capture the ovum expelled each month by the ovary and directed towards the sperm, which rises in the opposite direction. In this way, although endometriosis does not necessarily cause infertility, it can, in some cases, make it difficult for pregnancy to occur.
What are your symptoms?
The main symptoms are: very painful periods due to the flow of blood from the endometrial deposits located in areas where they have no outlet. Intimate relationships can also be painful at times.
Endometrial deposits can also form small, hard balls in the tissue under the uterus and in front of the rectum. This can be easily detected by the gynecologist in the course of a vaginal examination. If for theOn the contrary, endometriosis develops in the walls of the uterus, this organ can dilate or tighten.

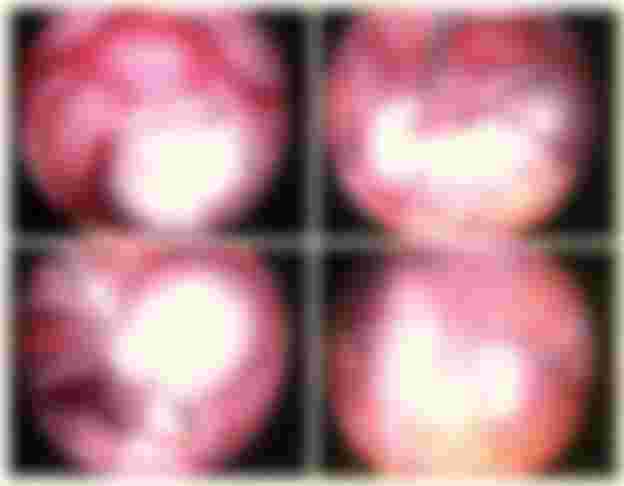
If a woman has doubts about whether she has endometriosis, the doctor may advise her to stay in the hospital for a laparoscopy. This test examines the uterus and other reproductive organs under general anesthesia by inserting a lighted instrument (similar to a telescope) into the abdomen through a small cut made under the navel. This test is also often done under local, soothing anesthesia.
Possible treatments
Doctors almost always try hormonal treatment first. What is almost always chosen is progesterone, which inhibits the activity of the mucosa that lines the uterus. Recently, other drug-based treatments are also being used that can totally cure this problem.
They are usually prescribed under strict doctor's prescription and supervision and sometimes must be used for six consecutive months. These treatments almost always cause the loss of menstruation at that time and also thus avoid a possible pregnancy. Another procedure to be a minor operation or therapeutic curettage to clean the active endometrial points and their deposits

Perhaps many women, due to ignorance, suffer from it and do not know what it is about! Let's take care.