Human evolution
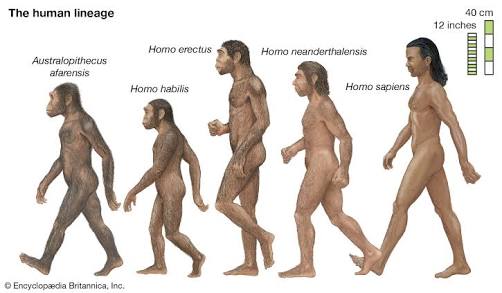
Human evolutionary is the evolutionary process by which modern human,begging with the evolutionary primates.Evolution does not change individual. Instead, it changes the inherited means of growth and development that typify a population (a group of individuals of the same species living in a particular habitat). Parents pass adaptive genetic changes to their offspring, and ultimately these changes become common throughout a population. As a result, the offspring inherit those genetic characteristics that enhance their chances of survival and ability to give birth, which may work well until the environment changes. Over time, genetic change can alter a species' overall way of life, such as what it eats, how it grows, and where it can live. Human evolution took place as new genetic variations in early ancestor populations favored new abilities to adapt to environmental change and so altered the human way of life.Evolution involves the gradual changes from simple to more complex forms. Humans are believed to have developed from simpler forms.Evolution is the outcome of the interaction between the following five processes:
Mutation.
Genetic Recombination.
Chromosomal Abnormalities.
Reproductive isolation.
Natural Selection.
ohoh