THE BASIC METHODS TO BE LEARNED ON HOW TO INSTALL WIRING (WIRING INSTALLATION)
Joining Box

In this installation method, connections to any appliances are prepared through joints. The joints are made from joint boxes using appropriate connectors and joints cutouts. This method of wiring doesn’t consume cable sizes. Electrical experts have to take note that this installation might be expensive in a few cases. Structure for this system will be made easier using builder trends software. It’s a trend that must be considered by electrical contractors.
Looping System

This wiring installation method is universally used in any electrical method. Other appliances and lamps are connected in a parallel position so that every appliance can be separately controlled. When the connection is required, the feed conductors are being lopped in by getting it directly to the terminal and then fetching it forward again to the next points.
The light and switch feeds are carried around the circuit by a series of loops. It will be carried around from one point to another until the last on the circuit is reached. The line or phase conductors are lopped either in a box or switchboard.
4 BASIC ELECTRICAL WIRING TECHNIQUES
CASING AND CAPPING WIRING
In this wiring type, the cable will run through a wood casing with parallel grooves appearing at regular intervals. The case is expected to be fixed to either walls or ceilings using screws. It will then be fully covered with a cap to protect the wires. This system is considered to be considerably expensive, yet there is a huge possibility of short circuit risks resulting in some fire hazards. Electrical contractors need to trace possible hazards earlier. The best way to handle bombarding issues is through the application of construction scheduling software.
Listed below are the materials used for casing wiring:
· PVC or VIR insulated wires
· Capping (wood or plastic made)
· Capping or casing joints
· Casing enclosure (wood or plastic made)
Advantages of this type of wiring scheme are:
· Strong and durable wiring
· Inexpensive and easy to install
· Any wiring customization can be done
· Safe from dust, rain, smoke and steam
CLEAT WIRING
Here, cables that are PVC insulated are being used. The cables will be fasted directly to the walls using wood, porcelain or plastic cheats. Everything will be installed at different intervals, usually 6km. apart. This wiring is affordable but usually good enough for temporary applications. It isn’t even suitable for residential electrical wiring.
Listed below are some of the common materials used in cleat wiring:
· Weatherproof cables
· Lots of screws
· PVC or VIR insulated wires
· Plastic cleats or porcelain cleats (2-3 grooves)
This type of wiring has some advantages:
· East for detecting faults
· Easy to repair
· Addition and alteration is easy
· Easy and Cheapwiring
BATTEN WIRING

One of the most important wiring methods applied today is the batten wiring. In this wiring, insulated wires will run through the wooden battens. The battens are fixed on walls and ceilings using either screws or plugs. The cables are fitted directly onto the battens. Link clips are used as well and it will be fastened with rust-resistant nails.
Basic materials used for batten wiring are the following:
· TRS or CTS cables
· Tinned brass buckle clip (link clip)
· Brass pins
Advantages of this type of wiring scheme are listed below:
· Installations are way easier
· Appearance is much better
· Cheaper material costs
· Easy and flexible customization
· Lesser chances of leakage current
CONDUIT WIRING

PVC cables are often used in conduit wiring. If the pipes are running through the ceilings and wall surface, surface conduit wiring is the best term. On the other hand, if pipes run inside the wall surface and it will be covered with plastering, it is termed as concealed conduit wiring. Surface wiring is used mainly for industrial applications in order to interlink heavy motors. Lastly, concealed wiring is utilized for residential purposes.
Materials used for conduit wiring:
· Metallic conduit (class A and B)
· Non-metallic conduit
· PVC or VIR insulated cables
· Coupling
· Screws
· Rigid offset
FEATURES OF AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
THE ENERGY SOURCE

In an electrical circuit, the power source provides the voltage (the force that pushes electrons through a conductor -- measured in volts) and current (the rate of flow of electrons -- measured in amperes) to energize a device attached to the circuit.
A voltage power source provides a constant voltage level to the circuit. Examples of voltage power sources are batteries, like the ones in your laptop computer or car, the energy from the solar panels on your roof, your car's alternator, or the energy coming from your local power plant or hydroelectric dam.
On the other hand, a current power source which is measured in amps, provides a constant current of energy regardless of its voltage. Typically, constant-current circuits are included in a system to protect the device providing the electrical load on the circuit. For example, an LED requires a constant level of current to protect it from burning out or being damaged.
THE CONDUCTOR

In a typical electrically powered environment that uses common electrical devices, the conductor is the wiring in a home or device that provides the path of the circuit, on which the energy flows. The conductor (conduction) system interconnects all of the other parts of the circuit.
Electrical power flows somewhat like water through a pipe or hose. The conductor provides the piping through which the electrical energy flows from its source to its load and back again sometimes .And like water through a hose.
THE SWITCH

The switch provides the control that closes (continues) or opens (breaks) the electrical energy flow on the circuit. A variety of circuit switches exist, including wall switches, push buttons, key toggles, and many biometric devices.
A closed circuit switch can have either a sustained contact or a transient contact. A sustained contact, such as a light switch, maintains the circuit in a state that allows for a constant flow of energy. A transient, or momentary, contact only provides an energy flow to the circuit while a button or similar device is being pushed or engaged. When the button is released, the circuit is once again open.
THE LOAD

Any device attached to an electrical circuit that is activated or energized by the flow of electricity to it, provides the electrical load on the circuit. The load is the amount of electrical energy the device uses to complete its task.
This electrical consumption is measured in watts, which equals the current (amps) multiplied by the volts on the circuit. Lights, TVs, motors, heaters and appliances are load devices that consume power.
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM

A schematic is defined as a picture that shows something in a simple way, using symbols. A schematic diagram is a picture that represents the components of a process, device, or other object using abstract, often standardized symbols and lines. Schematic diagrams only depict the significant components of a system, though some details in the diagram may also be exaggerated or introduced to facilitate the understanding of the system.
Schematic diagrams do not include details that are not necessary for comprehending the information that the diagram was intended to convey. For example, in a schematic diagram depicting an electrical circuit, you can see how the wires and components are connected together, but not photographs of the circuit itself.
For example, if you are taking the subway you may see a “map” showing you all the stations along a subway line, but that map will not show all the roads and buildings you may pass along the way. In this case, the entire subway system can be represented as differently colored lines depicting the different subway routes, with dots indicating the stops along the lines.
WIRING DIAGRAM

A wiring diagram is a simplified conventional pictorial representation of an electrical circuit. It shows the components of the circuit as simplified shapes, and the power and signal connections between the devices.
A wiring diagram usually gives information about the relative position and arrangement of devices and terminals on the devices, to help in building or servicing the device. This is unlike a schematic diagram, where the arrangement of the components' interconnections on the diagram usually does not correspond to the components' physical locations in the finished device. A pictorial diagram would show more detail of the physical appearance, whereas a wiring diagram uses a more symbolic notation to emphasize interconnections over physical appearance.
A wiring diagram is often used to troubleshoot problems and to make sure that all the connections have been made and that everything is present.
20 EXAMPLES OF ELECTRICAL MATERIALS
1. ELECTRICAL CONDUITS FITTINGS
Electrical conduits are metal, plastic or fiber pipes designed to protect electrical cables and wires. They’re used in just about every residential and commercial establishment, especially for wiring that is either exposed, or fitted outdoors. Since they are essentially a safety feature, you should select the material, size and fittings based on the environment of the installation and the type of wiring it’ll be housing.
2. EXPLOSION PROOF ENCLOSURE
Explosion Proof is a product design to contain an electrical short so that it doesn’t ignite a hazardous atmosphere causing an explosion. Refineries, gas stations, paint booths are examples of where these products would be used. They are heavy duty steel or aluminum by design, or can be fiberglass as well.
3. CIRCUIT BREAKERS
Circuit Breakers are devices that automatically interrupt the follow of an electric current to protect against a short or overload. Circuit Breakers are made by several manufacturers including Cutler Hammer/ Westinghouse, General Electric, Square D, ITE Sieonans, and Federal Pacific. Circuit Breakers protect the smallest house circuit to the largest industrial requirements.
4. ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
Electrical Connector is a part that will join or adapt one part to another. Connector range in size from 3/8″ to 6″. They can be indoor, outdoor, corrosive protected or explosion proof.
5. ELECTRICAL BOX
Electrical Box is an enclosure used for many purposes such as pulling, connecting or terminated an electrical circuit. Electrical box can be set screw or indoor; it can be rain tight, or outdoor. They can be made of steel, aluminum, plastic, stainless steel, or cast iron. Requirement can include corrosive protected or explosion protected by design.
6. LUGS
Lugs are the electrical connectors that terminate the electrical circuit. Lugs are made of copper, aluminum, or bronze. They are made for the smallest wire size, 26 gauge to the largest 2000 MCM. Lugs can be mechanical or set screw; compression or crimp, solder or weld; or clamp type. T&B, Burndy, Penn Union, Panduit, and 3M are some different manufacturers of lugs.
7. MOTOR CONTROL
Motor Control is an apparatus used to regulate a motor or mechanism. It can control the smallest mechanism to the largest power turbines. There are several manufacturers of motor control including Allen Bradley, Square D, Cutler Hammer, ITE Siemens, General Electric and Westinghouse.
8. CONVENIENCE OUTLET
This electric material acts as a convenient source of electric energy for electrical appliances which requires electricity to work. The male plug of the appliances is connected to this material. It could be simplex, duplex, or multiplex it may be surface or flush type.
9. MALE PLUG
The male plug is a device that is used to connect the electrical appliance to the convenience outlet. The convenience outlet will act as a source of electrical energy and the male plug is attached to a flat cord. One end of the cord is connected to the male plug and the other end is connected to the appliance.
10. LAMP HOLDERS
Lamp holders are a device that is used to hold the lamp they are also called lamp sockets and receptacles. These lamp holders are in any size and in many designs.
11. SWITCHES
Switches are used to control the flow of electric current in a circuit they are used to connect and disconnect the flow of electric current in a circuit. Switches are in many shapes and sizes.
12. FUSES
A fuse can be considered as a circuit protection device that automatically blows and cuts the current when a short circuit happens. So if there is an overvoltage the switch will cut the current and protects the device.
13. CIRCUIT BREAKER
A circuit breaker is also a protective device that will protect the appliances from over-voltages. The circuit breaker will automatically blow and cuts when short circuit or overvoltage occurs.
14. JUNCTION BOX
Junction boxes are electric materials where connections or joints of wires are done. Junction boxes are mostly made of metal or plastics.
15. UTILITY BOX
Utility boxes are made up of metal or plastic material, utility boxes are attached with the flush type convenience outlet and switch.
16. FLAT CORD
It is a duplex stranded wire which is used for temporary wiring installations and they are commonly used in extension cord assembly.
17. ELECTRICAL WIRE
Electrical wire is a conductor which is used for the transfer of electricity, the electric wire is the basic material for electrical installations. The transfer of current from source to load is possible with the help of an electric wire. Stranded electric wires are made up of multiple strands joined together and solid wire is made up of a single strand of wire which is either made up of copper or aluminum. These are used in wiring installations.
18. CONDUITS
Conduits are electrical materials which are used for the safe passage of wires, it does the protection and insulation of the wires. There are many types of conduits like rigid metallic, flexible metallic conduit
19. CLAMPS AND CONNECTORS
Clamps are electric materials that are used to hold and anchor electrical conduits to their proper position. While the connectors are used to attach the metallic or non-metallic conduit to the junction or utility box.
20.VC CONDUIT PIPE PVC Conduit Pipe
VC conduit Pipe PVC conduit pipe are popular type of electrical conduit used for above ground and underground applications. These conduits are made of high quality PVC and are flexible in nature. The pipes have high electrical strength and impact resistance.
SCHEMATIC AND WIRING DIAGRAM
A. Schematic and wiring diagrams (SWD) for three-duplex receptacle connected to a main breaker in parallel.
· SCHEMATIC & WIRING DIAGRAM

B. SWD for three ceiling lights, the two lights is controlled by a single switch and the other one is controlled by a single switch.
· SCHEMATIC & WIRING DIAGRAM
C. SWD for a duplex outlet connected parallel to a light controlled by a three-way switch that passes a common junction box.
· SCHEMATIC & WIRING DIAGRAM

D. SWD for a ceiling light controlled by a switch, individual outlet for AC and Electric water pump in Parallel.
· SCHEMATIC AND WIRING DIAGRAM

E. SWD for a 5-light in series connected to a battery charged by a solar panel.
· SCHEMATIC AND WIRING DIAGRAM

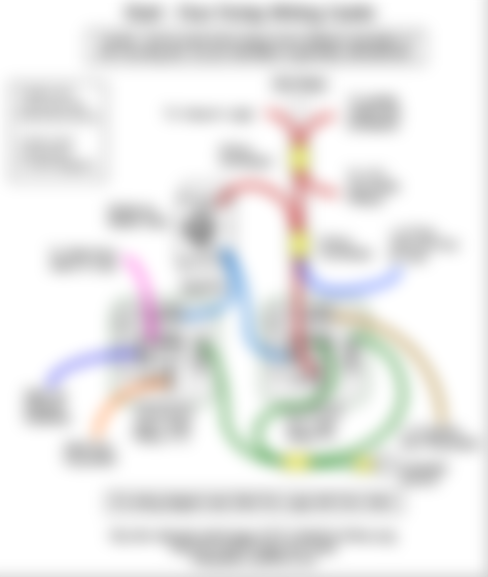
GROUNDING
Grounding offers excess electricity the most effective and safest route from an appliance back to the ground by way of an electrical panel. Electrical grounding is a backup pathway that is generally only used if there is a fault in the wiring system.
One of the most important reasons for grounding electrical currents is that it protects your appliances, your home and everyone in it from surges in electricity. If lightning was to strike or the power was to surge at your place for whatever reason, this produces dangerously high voltages of electricity in your system.
REASONS FOR GROUNDING
Protection against electrical overload
One of the most important reasons for grounding electrical currents is that it protects your appliances, your home and everyone in it from surges in electricity. If lightning was to strike or the power was to surge at your place for whatever reason, this produces dangerously high voltages of electricity in your system. If your electrical system is grounded, all of that excess electricity will go into the earth — rather than frying everything connected to your system.
Helps direct electricity
Having your electrical system grounded means you will be making it easy for power to be directed straight to wherever you need it, allowing electrical currents to safely and efficiently travel throughout your electrical system.
Stabilizes voltage levels
A grounded electrical system also makes it easier for the right amount of power to be distributed to all the right places, which can play a huge role in helping to ensure circuits aren’t overloaded and blown. The earth provides a common reference point for the many voltage sources in an electrical system.
Earth is the best conductor
One of the reasons why grounding helps to keep you safe is because the earth is such a great conductor, and because excess electricity will always take the path of least resistance. By grounding your electrical system, you are giving it somewhere to go other than into you– possibly saving your life.
Prevents damage, injury and death
Without a properly grounded electrical system, you are risking any appliances you have connected to your system being fried beyond repair. In the worst-case scenario, an overload of power can even cause a fire to start, risking not just extensive property and data loss but physical injury as well.









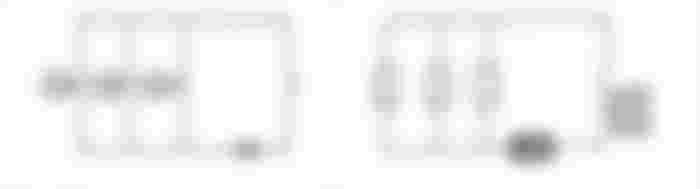
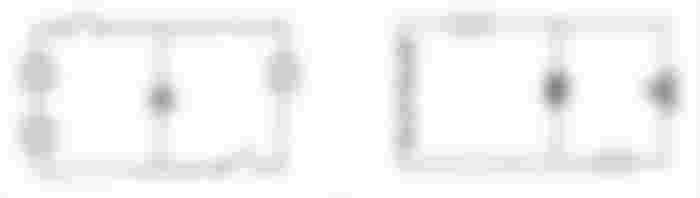


Hello! I see you are posting this informative article, that can be used by people who need it. We appreciate it! However, if it's okay to say, I have noticed that there is one portion where all of the words seemed to stick together, without spaces. It is in the "Earth is the best Conductor" part. :))