ELETRIC MOTOR AND THE PRINCIPLE APPLIED IN ITS OPERATION

An electric motor is an electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Mechanical energy is used to rotate pump impeller, fan, blowers, drive compressors and lift materials. It is used extensively in such diverse systems as household appliances, automobiles, computers, printers, and automatic cameras.
Electric motors involve rotating coils of wire which are driven by the magnetic force exerted by a magnetic field on an electric current.
HOW DOES AN ELECTRIC MOTOR WORKS?

CLASSIFICATIONS OF ELECTRIC MOTORS AND ITS FRAMEWORK
According to type of source:
DC MOTOR
A DC motor is a mechanically commutated electric motor powered from direct current (DC). The stator is stationary in space by definition and therefore its current. The current in the rotor is switched by the commutator to also be stationary in space. This is how the relative angle between the stator and rotor magnetic flux is maintained near 90 degrees, which generates the maximum torque.
Two types of DC Motor:

Ø Brushless DC electric motor (BLDC motors, BL motors) also known as electronically commutated motors (ECMs, ECmotors) are synchronous motors that are powered by a DC electric source via an integrated inverter/switching power supply, which produces an AC electric signal to drive the motor (AC, alternating current, does not imply a sinusoidal wave form but rather a bi-directional current with no restriction on waveform); additional sensors and electronics control the inverter output amplitude and wave form (and therefore percent of DC bus usage/efficiency) and frequency (i.e. rotor speed).

Ø Brushed DC motor is an internally commutated electric motor designed to be run from a direct current power source. Brushed motors were the first commercially important application of electric power to driving mechanical loads, and DC distribution systems were used for more than 100 years to operate motors in commercial and industrial buildings. Brushed DC motors can be varied in speed by changing the operating voltage or the strength of the magnetic field.
AC MOTOR

An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). It commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stationary stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft that is given a torque by the rotating field.
Two types of AC motor:
Ø Induction Motor or Asynchronous Motor. The magnetic field on the rotor of this motor is created by an induced current.
Ø SynchronousMotor, which does not rely on induction and as a result, can rotate exactly at the supply frequency or a sub-multiple of the supply frequency. The magnetic field on the rotor is either generated by current delivered through slip rings or by a permanent magnet. The induction motor is running slightly slower than the synchronous motor because its speed is reduced by the slip. Therefore, it is also called asynchronous motor.
UNIVERSAL MOTOR

Universal motors are small series motors up to 3.73 kW rating which are commonly designed to operate on either direct current or alternating current.
According to intended use or special characteristics:
Ø Gear motor – is a motor that has a gear train built into the motor housing to reduce the output shaft speed and increase the shaft torque.
Ø Synchronous motor – type of motor in which shaft rotation is in exact synchronization with the frequency of the power source. These motors are either single phase or polyphase (usually three phase)ac motors.
Ø Multispeed motors – are motors with two or more fixed speeds. Its operation is often obtained by having either a tapped motor winding or a separate motor winding for each speed.
Ø Variable Speed motors – motors whose speed is continuously variable and is typically controlled by varying the voltage and/or frequency of the power source.
Ø Torque motors– motors designed to provide maximum or near maximum torque when the motor is stalled and still be able to operate for an extended period of time without overheating.
According to power rating:
Ø Sub-fractional horsepower –motor ratedlessthan1/20hpor usually expressed in mill horsepower .
Ø Fractional horsepower –motor rated from 1/20 hp to 1 hp.
Ø Integral horsepower –any motor rated above 1 hp.
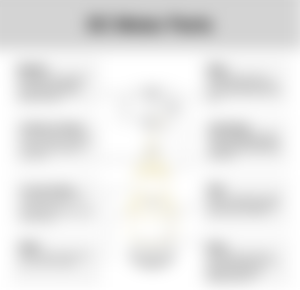
TYPES, CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS OF SINGLE-PHASE AND THREE-PHASE AC AND DC ELECTRIC MOTOR



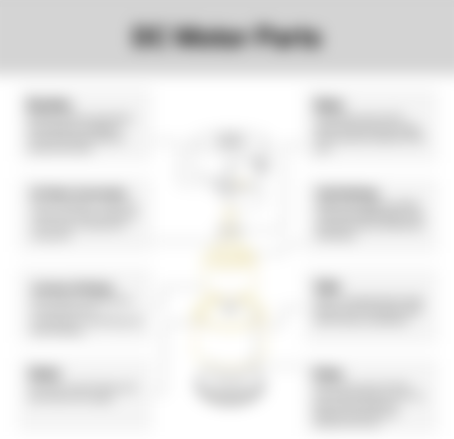





Electric motors play a pivotal role in modern agricultural and biosystems systems, enhancing efficiency and productivity. These motors drive various machinery, from irrigation pumps to automated feeding systems, ensuring smooth operations across diverse tasks. For those seeking reliable solutions, https://lam365.com offers a comprehensive range of high-performance electric motors tailored to meet the unique demands of agricultural settings. By integrating these advanced motors into their systems, farmers and biosystems professionals can achieve greater precision, reduce operational costs, and support sustainable practices in their daily operations.