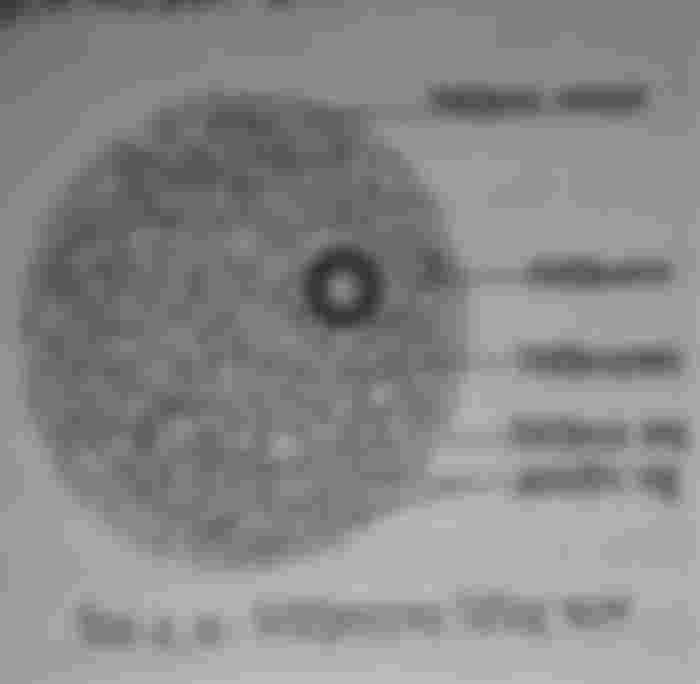
Although quite small in size and volume, the structure and function of the cell is quite complex. An ideal plant cell consists mainly of two parts - the cell wall and the protoplasm
Cell wall and cell membrane: The cell wall is the outer layer of the cell. It is made of inert cellulose and is a unique feature of plant cells. Animal cells have no cell wall. The cell wall gives the cell a certain shape and firmness. The fine elastic, living membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell is called the cell membrane. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances inside and outside the cell.
Protoplasm: Protoplasm is the main building block of the cell. The water content is about 85 to 95 percent. The nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, etc. are floating or sinking in the protoplasm. Protoplasm is composed of organic matter like carbs, sugars, lipids etc. Among the inorganic substances are minerals and gases dissolved in water. All the work of the cell is done in the protoplasm. It is usually dynamic and capable of reproduction.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the part of the protoplasm that surrounds the nucleus. It is mainly made with meat. The major organs of the cell in the cytoplasm are discussed below
Mitochondria: The respiratory organs of mitochondrial cells. The mitochondria are the only source of energy needed to manage the cell's biological function. That is why it is called the powerhouse of the cell. It plays a major role in the management of all oxygen transport and respiratory functions. Mitochondria look round, rod-shaped or thread-shaped. They are scattered in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells. The mitochondria are made up of two layers. The outer covering is smooth but the inner covering is folded in various ways and hangs on the inside. The hanging folds are called Christie's. Mitochondria contain about 63% protein, 25% lipids and 0.5% RNA. The semi-liquid granular material inside the mitochondria is called matrix.

Cell cavity: A cavity filled with fluid surrounded by a single membrane in the cytoplasm is called a cell cavity. Water, organic acids, sugars, mineral salts etc. are stored in the cell cavity. Plant cell cavities are quite large and cover most of the cell space. The cells of animal cells are very small in size but large in number. It acts as a storehouse of cells.
Plastids: The organelles that are pigmented or colorless in plant cells are called plastids. Plastids are one of the unique features of plant cells. Due to its presence, the leaves, flowers and fruits of the plant can be seen in a variety of colors. Plastids that contain green chlorophyll are called chloroplasts. The leaves of the plant look green for chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll helps in photosynthesis.
Plastids with colors other than green (red, yellow) are called chromoplasts. It contains a lot of carotene and xanthophyll. Flowers and fruits come in different colors for chromoplasts. And because of this, insects and butterflies are attracted to flowers and pollinate. Colorless plastids are called leukoplasts. It is found in the lower part of the soil of plants (mainland stems). It stores food.
Nucleus: The most dense, almost spherical cell organelle of the protoplasm is called the nucleus. The nucleus controls all the biological functions of the cell. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a fine living covering. This living coating is called nuclear coating. The nucleoplasm is a fluid made of protein inside the nucleus. One or more bright dense spherical objects in the nucleus is called nucleolus. The nucleolus participates in cell division. Some of the long thread-like objects found in the nucleus are chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of many very fine genes. The chemical component of a gene is DNA. Through genes, various characteristics of an organism, such as body size, volume, color, sex, etc., are transmitted from parents to offspring. That is why chromosomes are called the bearers and carriers of heredity.

The nucleus controls all the biological functions of the cell. Cells cannot survive without the nucleus. That is why it is called the heart of the cell. Each human body cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes. Of these, 22 pairs control the anatomy and biological functions, while the remaining one pair determines the sex of the child. X chromosomes are the two sex-determining chromosomes in the deployed cells of females. But in men, one is X and the other is Y chromosome. During female ovulation, each egg attains one X chromosome along with the other chromosomes. But during male sperm formation, half of the sperm acquires the X chromosome and the other half acquires the Y chromosome. If the X chromosome-carrying sperm fertilizes the egg during pregnancy, the chromosome of the fertilized egg will be X and the child will be a daughter. On the other hand, if the sperm carrying Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the chromosome of the fertilized egg will be X Y and the child will be a son.
A significant difference between plant cells and animal cells is that plant cells have an inert cell wall made of cellulose outside the plasma membrane but the cell cell has a plasma membrane, not a cell wall. It is also noteworthy that plant cells usually contain plastids, not living cells. As the cavity in the plant cell becomes larger, the nucleus is located on one side of the cell. On the other hand, cell cavities are very small and much larger in number. As a result, the nucleus is in the center of the cell. In plant cells, sugars are stored as starch, but in animal cells, sugars are stored as glycogen. Plant cells do not have centrosomes, but animal cells always have centrosomes.