This is one of the serious problem we should mind. And take action of.
What is greenhouse gas?
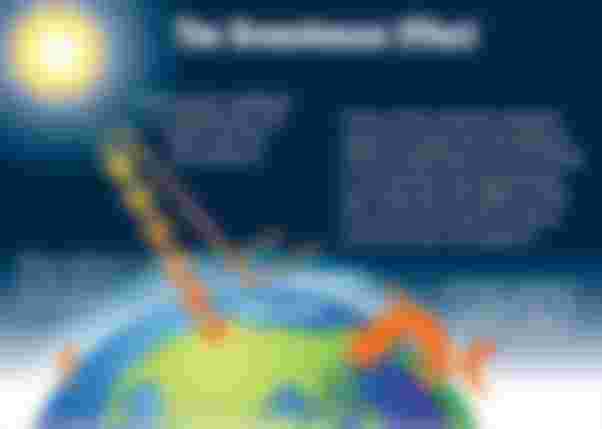
A greenhouse gas refers to an atmospheric gaseous substance that can sufficiently absorb infrared radiation. Obviously, greenhouse gases got their name from the typical greenhouse used during plant cultivation.
Greenhouses can maintain temperature because of the transparent glasses that favor the entry of sunlight. This sunlight then warms the air inside the structure but does allow this warmed air to get out.
Such phenomenon is similar to the atmospheric greenhouse effect. During a greenhouse effect, the molecules of these greenhouse gases absorb the heat and reflect them to the surface. Because of this, the temperature in the Earth’s atmosphere and land surface increases.
Hence, with greater amounts of atmospheric greenhouse gases, more radiation will be reflected back, causing an increase in temperature.
Naturally, a greenhouse effect is considered to be an essential phenomenon that helps in the maintenance of the Earth’s temperature. Without it, the planet’s temperature would fall to just -18° Celsius, as compared with +14° Celsius. At this point, the greenhouse effect should not be considered as a synonym of global warming.

Types of Greenhouse Gases
In general, greenhouse gases constitute just almost 1% of the total gases present in the atmosphere. Their concentrations are dependent on the balance between the “sources” and “sinks” that function to create and destroy these gases respectively. Anthropogenic activities tend to increase these concentrations by either introducing new types of gases in the air or intervening with the sinks.
The most abundant greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and chlorofluorocarbons. Additionally, atmospheric water vapor also contributes to the occurrence of the greenhouse effect. Fortunately, its cause is believed to be non-anthropogenic.
Since the industrial revolution, the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere have increased significantly. Alarmingly, the increase has resulted in a so-called radiative-forcing effect where heat is trapped inside the Earth’s atmosphere, thereby contributing to the increase in global temperature.
The increase in the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) accounts for more than half of this effect, compared with other gases like methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (NO), ozone (O3), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which account for 16%, 5%, 12%, and 12% respectively.
However, according to scientific studies, methods to reduce the production of greenhouse gases and emission of aerosol should not be assumed to decrease the impacts of climate change rapidly.
Characteristics of Greenhouse Gases
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Burning of fossil fuels
Deforestation
Plants undergoing photosynthesis
Oceans
Absorption of infrared radiation
Indirectly affects the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere.
Methane (CH4)
Burning of Biomass
Rice paddies
Fermentation by enteric bacteria
Microorganisms uptake
Reactions associated with hydroxyl groups
Absorption of infrared radiation
Indirectly affects the concentration of ozone and water vapor in the stratosphere
Production of carbon dioxide
Nitrous oxide (N2O)
2Burning of Biomass
Combustion of fossil fuels
Fertilizers
Removal by soils
Photolysis in the stratosphere
Absorption of infrared radiation
Indirectly affects the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere
Ozone (O3)
Chemical reactions that involve oxygen
All catalytic chemical reactions that involve nitrous oxide, hypochlorite, and hydroxyl species
Absorption of infrared and ultraviolet radiation
Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)
Industrial production
Photolysis and reaction with oxygen
Absorption of infrared radiation
Indirectly affects the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Plant emissions
Man¬made release (transport & industrial)
Soil uptake
Reactions with OH
Affects stratospheric O3and OH cycles
produces CO2
Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
Volcanoes
Coal and Biomass burning
Dry and wet deposition
Reactions with OH
Forms aerosols, which scatter solar radiation.
Effects of Too Much Greenhouse Gases in the Atmosphere
Climate change, as its name suggests, refers to the change in the weather pattern distribution in the Earth’s atmosphere. Alarmingly, this change can last for a long period and after reaching a certain threshold can become irreversible.
Unfortunately, greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect are the number one drivers of climate change. The following are some of the most common effects of greenhouse gases.
1. Global Warming
As alluded to earlier, the greenhouse effect is not synonymous with global warming, but rather a phenomenon caused by it. The increase in the amounts of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere reduces the out-flux of infrared radiation, resulting in a warmer temperature. Changes in the Earth’s temperature will trigger other phenomena like changes in wind patterns and variation of cloud covers.
2. Rise in Sea Level
Aside from those that were mentioned above, global warming can also cause the rise in sea level. The increase in temperature results in the thermal expansion of seawater and melting of the ice and glaciers in some regions like Greenland and Antarctica, thereby adding water to the total water in the ocean. Several studies are predicting that if global warming continues, the Earth’s sea level will become ten times higher (from 0.09 meters to 0.88 meters) in the next 90 years.

3. Effects on Biological Cycles
Because of higher temperatures, it is expected that biological cycles will be affected as well. One of the most affected is the hydrological cycle. Because the atmosphere becomes relatively warmer than it was, the amount of evaporation is also expected to increase. In other words, this means that higher amount of precipitation will be experienced. On the other hand, global warming also contributes to the loss of coastal areas and other habitats, thereby reducing organism population and diversity.

4. Economic and Agricultural Impacts
Because of higher carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, photosynthesis can readily occur, making plants grow at a faster rate. However, too much heat can also affect soil and water conditions, thereby causing them to wilt and eventually die. When this happens, agricultural growth will be affected.

That's the effect of greenhouse gas to our nature. We must avoid doing the things that can cause greenhouse gas. Let's save our mother nature.
@TheRandomRewarder I hope you like my article.
Sir @ErdoganTalk , @Omar I hope you will like my article.




