Coitus interruptus
Also called ‘withdrawal’. A contraceptive method where the penis is withdrawn from the vagina before ejaculation so that no semen can enter the cervix. As a means of contraception, this method is generally unreliable (about 20 percent failure rate), although many couples have successfully used it to space their children.

Colic
A severe, cramping pain in the abdomen, caused by spasm of muscles in the wall of hollow organs. Colic may be caused by constipation or distension of the bowel; any disorder that irritates the intestine, such as infection and certain poisonings; and partial or complete obstruction of the bowel. Biliary colic is due to obstruction of the bile ducts, usually by a gallstone. Urinary colic is due to obstruction of the ureter by a stone or tumor.

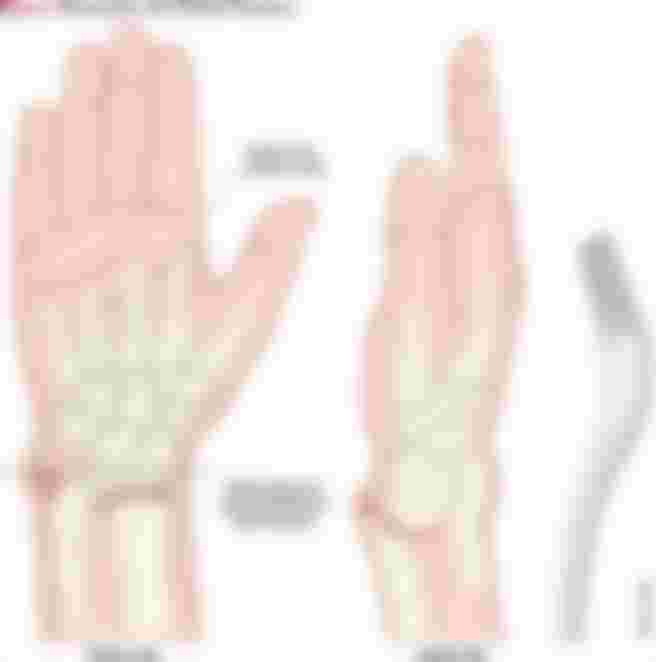
Colles’ Fracture
A fracture of the forearm bones, just above the wrist. It is often caused by a fall on to the outstretched hand.

Colon
The lower part of the digestive tract. The colon and the rectum make up the large intestine, where water is absorbed from food residue, which is then discharged as feces.

Colostomy
A surgical procedure in which an artificial opening, or stoma is made in the wall of the abdomen and connected to part of the colon. The contents of the large bowel are expelled into a colostomy bag attached to the stoma, instead of passing out through the rectum. A colostomy may be performed when part of the colon or rectum is removed because of cancer, and in certain diseases of the large bowel.

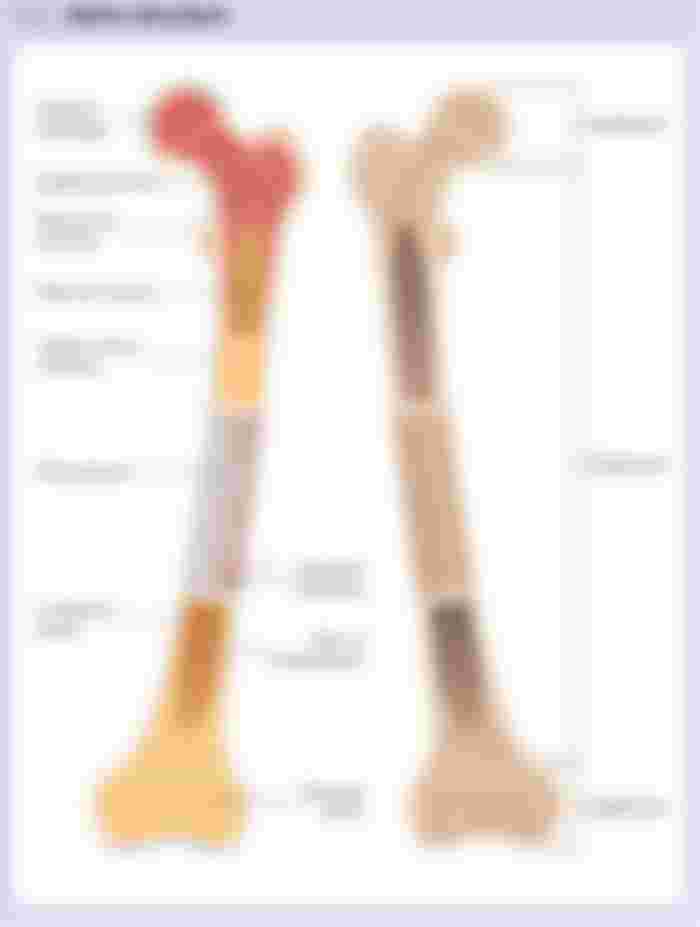
Bone
The hard, dense tissue that makes up the skeleton which is the framework of the body. The bones of the central skeleton form the head and trunk and the bones of the peripheral skeleton form the arms and legs.

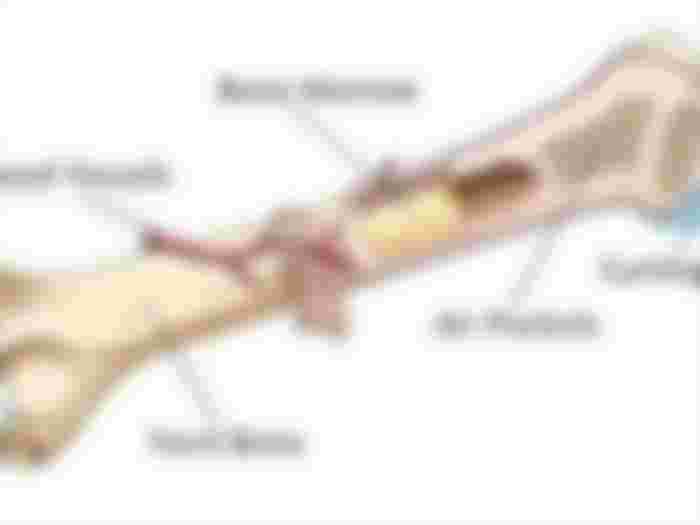
Bone Marrow
The soft core of bones. It consists of tissue specialized for the production of blood cells (hemopoieses). Sometimes a sample of bone marrow is taken to help in the diagnosis of a blood disorder.