In October 2008, a person using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the results of a study on the web. The title of the study was "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System". during this study, he gives ideas on the way to transact in any a part of the planet without the assistance of any bank or intermediary. This method explains that it's possible to send money directly from one user to a different.
As a results of his research, the primary bitcoin market was launched in January 2009. Satoshi Nakamoto was the primary to make software for bitcoin mining. consistent with his pseudonym, the Bitcoin unit was named Satoshi. 100,000,000 (ten crore) Satoshi equals 1 bitcoin.

Bitcoin may be a sort of digital currency. Bitcoin is formed from complex mathematical calculations that are run seamlessly by many computer users. These managers are called miners. the govt of the country has no control over this currency. So it's very fashionable with hackers and sellers of darkweb. Bitcoin isn't illegal. Bitcoin has not yet been banned in any country. But there's little risk in using it. For Bitcoin transactions, both the customer and therefore the recipient need to believe a 3rd party. The miners are the third party here.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin may be a currency that's completely virtual. It can save its own value, no need for banks or the other institution to save lots of bitcoin later. Bitcoin behaves like gold. It increases its depreciation a bit like gold and may be exchanged at any time. it's possible to earn tons of cash by saving bitcoin and selling it if the worth increases within the future. But the worth of Bitcoin doesn't increase all the time, sometimes the worth of Bitcoin also decreases.
Bitcoin is managed through a blockchain. Blockchain may be a very simple ledger. The blockchain is different for every user and his or her personal bitcoin wallet. All bitcoin transactions are recorded during a public ledger as proof of the transaction. This process helps protect people from bitcoin fraud. Bitcoin is registered within the digital wallet consistent with the name of the wallet, not within the personal name. this suggests that bitcoin transactions are often done anonymously. While nobody else are going to be ready to easily see your identity, they're going to be ready to see the transaction history of your Bitcoin wallet.
When Bitcoin is shipped to a Bitcoin wallet, it's pending moderation. If a minor transaction isn't approved, the bitcoin won't reach the opposite end of the wallet. Minor has got to pay some satoshi for this moderation. Anyone with a strong computer are often a bitcoin minor.
The common currency is regulated by the govt of the country. They produce new coins whenever needed. Bitcoin has no such specific rules. But there's a limit to Bitcoin making. Bitcoin production will automatically stop after the entire bitcoin worldwide reaches 21 million.
Anyone can make a new bitcoin. (foremost Successful Bitcoin Clone)
Around seven years ago, a near-clone of Bitcoin was created by former Google developer Charles Lee: a replacement cryptocurrency that shared most of its code with the higher known market leader. EOLBREAK Despite being like Bitcoin in virtually every way, Litecoin has managed to carve out its own culture, value proposition — and by market capitalisation nearly 2 percent of the whole crypto sector.
When did Litecoin separate itself from Bitcoin despite being nearly almost like it structurally, and the way are the 2 measuring up to every other in 2018? like most crypto-related questions, it's best to seem within the data for answers. Here's how the numbers on July 13, 2012, nine months after its public release, compared Litecoin to Bitcoin:

And this is often how those numbers have changed as of September 12, 2018:

To understand how these numbers have shaped Litecoin vs Bitcoin — and the way they’ll still influence the connection between these cryptocurrencies within the future — we'd like to interrogate three dimensions of their history:
The origin story
The infrastructure
The community.
What quite future for these cryptocurrencies can we expect, given the difference within the level of activity and support in their respective communities?
Digging into these dimensions tells us that when it first debuted, Litecoin had a robust, persuasive advantage — but it's unclear if that advantage will last long-term
Litecoin gave people another shot at capturing the worth of Bitcoin
Travel back with us to the crypto state in 2011, when Charles Lee first considered Litecoin's concept. Here's a context about what happened at the time:
A gentleman named Laszlo had proven Bitcoin’s commercial potential by spending 10,000 BTC to get two large pizzas in May 2010.
Bitcoin’s price had shot from slightly below $0.05 USD in July 2010 to a peak of just about $30 USD in June 2011 — a ~60,000% increase in but a year.
Bitcoin mining was getting beyond the reach of ordinary hobbyists, with application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) being built for the express purpose of mining increasingly computationally intensive blocks.
It was obvious to anyone listening that Bitcoin had the potential as a replacement value transfer tool— but it also looked to several as if that they had missed the chance to become an early Bitcoin adopter and capture its value. (They didn't skills much higher Bitcoin's value will go up!)
It was during this landscape that Charles Lee launched Litecoin. The new cryptocurrency had an easy and compelling value proposition: it’s almost exactly like Bitcoin, but better for daily commerce — and you'll pip out from almost the very moment it’s first created.
Instead of following within the footsteps of Satoshi and launching Bitcoin privately after mining on his own a minimum of a million, Lee was up front about his identity and launched Litecoin publicly after mining just 150 coins.
In this respect, it wasn't a nasty thing that Litecoin was almost an equivalent as Bitcoin. Bitcoin had already proven its usefulness: if someone were ready to create a blockchain that took Bitcoin's same fundamentals but optimized it even a touch bit further for that specific utility, people would have a second chance of a successful cryptocurrency "getting in on the bottom floor."
That's exactly what Lee intended to try to to with Litecoin, and it had been a hit within the short run: trading for about $0.03 USD in July 2012, Litecoin reached a price point of $40 USD in November 2013— an increase of over 130,000 percent.
Litecoin was built to be better for ordinary transactions
There are really just three main structural “tweaks” that creates Litecoin different from Bitcoin, each of which was meant to form Litecoin more accessible for everyday commercial use:
A different hashing algorithm.
More overall coins.
More frequently mined blocks.
Let’s consider the initial and ongoing impact of every one, in turn.
Democratizing mining
In the youth of Bitcoin, anyone could use their computer to mine new blocks — but the increase of ASICs and organizations that pooled their computational power together to mine BTC put this process outside of ordinary people’s reach.

Lee wanted Litecoin to be minable by anyone, so he implemented a special hashing algorithm of his own design to form LTC mining ASIC-resistant. instead of Bitcoin’s CPU-intensive SHA-256 algorithm, Litecoin uses the memory-intensive Scrypt algorithm. This difference made it much harder to style specialized computers for mining Litecoin — a minimum of, that’s how it had been when Litecoin first launched.
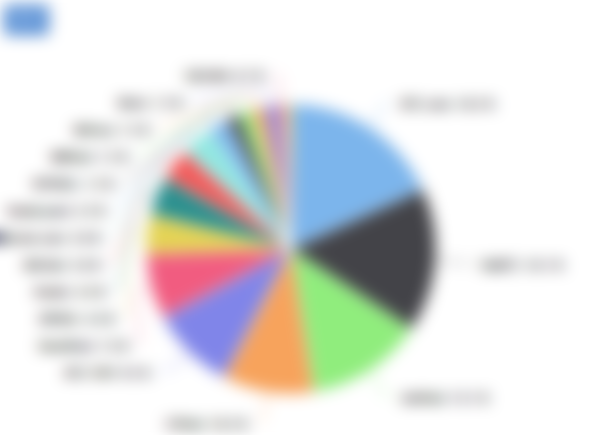
Nowadays, seven years later, it’s a special story: Litecoin-mining ASICs do exist, and that they dominate the mining scene. to urge a way of exactly what proportion they dominate, take a glance at the present hashrate distribution for the Bitcoin network as some extent of reference:
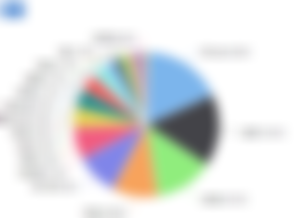
Accelerating confirmation times
What’s probably making the most important difference in Litecoin vs. Bitcoin today is that the incontrovertible fact that Litecoin adds new blocks roughly fourfold as frequently as Bitcoin does: roughly every 2.5 minutes, instead of every 10 minutes.
...and you will also help the author collect more tips.




You didn't actually bust the myth, rather proving that someone can make a new bitcoin. But it is not really a myth, anyone can make a new bitcoin. So therefore, I give you a small amount of mythbuster votes anyway.
10 votes