How your brain influences what you buy?
The market is a frightening place. ought to I get the skim or semi-skimmed milk? ought to I get the overpriced cut or a vegetarian alternative? Would my youngsters like this cereal or that one? the quantity of decisions and concerns is overwhelming, nevertheless several people go grocery searching on a weekly basis with relative ease. however can we do this?
In this article I’ll summarise some findings from my recent psychology Doctor of Philosophy, conducted at UCL and dunnhumby. I’ll discuss what I’ve learnt regarding client behaviour from the educational literature and the way large datasets of buying behaviour area unit revealing new insights regarding human noesis. I’ll conjointly discuss however psychological theories area unit serving to to raised justify and predict the alternatives created at the shelf-edge and the way this is often serving to dunnhumby to develop a additional personal understanding for patrons at scale.
Preferences within the work

Which complete would you choose? Experimental studies typically have faith in tasks that force participants to settle on between atiny low, mounted variety of choices represented across atiny low, mounted variety of expressly outlined attributes.
Psychologists like to study client decisions in straightforward work tasks. as an example, suppose you're asked to settle on a complete of bourbon liquor amongst the 2 choices within the table higher than. as a result of these brands distinction in quality and worth, you'll have a tough time selecting (usually, Associate in Nursing about equal variety of participants opt for complete A over complete B here).
Now suppose, a 3rd complete of liquor is introduced that's similar in quality however encompasses a considerably higher worth. that one would you choose?
Which complete would you select now? Have your preferences modified when the introduction of the new option?

After the introduction of this third “decoy” choice, the majority switch to complete B. Nothing regarding complete A or B has modified, nevertheless many of us switch their preference to complete B following the introduction of a fair costlier different.
These reversals area unit puzzling as a result of they recommend that our preferences for merchandise don't seem to be mounted. Rather, they're context sensitive, reckoning on the similarity to out there choices. If you’ve ever chosen between monthly subscriptions plans, mobile models or edifice rooms, you’ve doubtless knowledgeable these context effects within the wild.
Thinking outside the box
Not all decisions area unit like this tho'. within the market, we've got the liberty to settle on between tens of thousands of choices and might bundle them along in our own artistic ways in which. for every selection, we frequently retrieve attributes from memory (e.g., however a liquor tasted) and retrieve choices from memory (e.g., after we write a searching list). Moreover, our decisions area unit typically consecutive dependent, that means that what we decide currently might verify what we decide later.
This means that — we tend to|once we|after we} build decisions within the market — we trust heavily on the retrieval of knowledge from memory. {this is|this is typically|this can be} not one thing that's often captured in those extremely controlled experimental studies of client selection, that means we've got additional work to do!
A cornerstone of my analysis has thus been to leverage ideas regarding however folks learn, store and retrieve data from memory and use these to predict people’s decisions within the market. As I’ll show below, this has been amazingly effective.
The that means is within the use

Shoppers provide aiming to merchandise from their use with alternative merchandise. we all know that tomatoes area unit fruit, however we have a tendency to tend to consider them as going well with vegetables.
As we have a tendency to build additional decisions, we should always abstract some additional general, linguistics information regarding them. This helps US to reason regarding their similarity, amongst alternative things. as an example, while we all know that a tomato is technically a fruit, we have a tendency to area unit additional doubtless to suppose its role with alternative ingredients; a tomato are a few things that goes we have a tendency toll in an exceedingly salad! one in all my initial analysis queries was whether or not we have a tendency to may reverse engineer this linguistics information from people’s decisions directly; will we infer the forms of attributes and themes that shoppers use once wondering the numerous thousands of merchandise they expertise in store?
A similar question has been self-addressed by folks finding out linguistic communication process. process models like Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) learn wealthy linguistics themes or topics by finding out the co-occurrence of words in corpora of text. as an example, coaching Associate in Nursing LDA over a corpus of newspapers can eventually show that the words prime minister and parliament area unit terribly similar and sure belong to an equivalent topic (e.g., politics). These models will thus learn linguistics themes from people’s language.
In my initial project (published in process Brain & Behaviour), I borrowed these ideas to be told linguistics themes from shoppers’ decisions. rather than finding out word co-occurrences in sentences, we have a tendency to calculated the co-occurrence of market merchandise across one.2m real market receipts. The result was spectacular — when coaching the LDA model, we have a tendency to saw that it recovered coherent and infrequently purposeful. The topics ranged from terribly specific (e.g., stir-fry) to general (e.g., preparation from scratch). we have a tendency to even valid these topics employing a survey of a thousand real shoppers; our results supported the concept that these were closely aligned to the linguistics themes control in people’s heads.
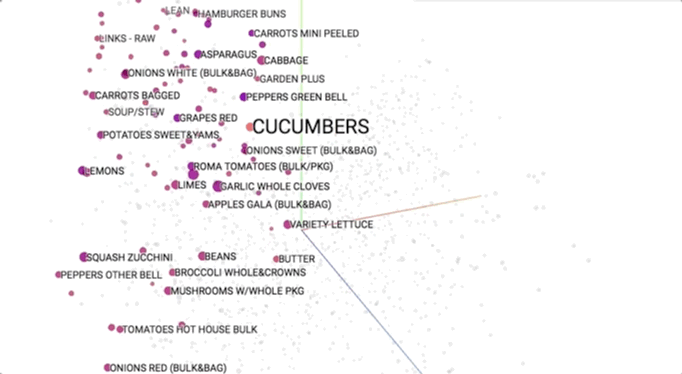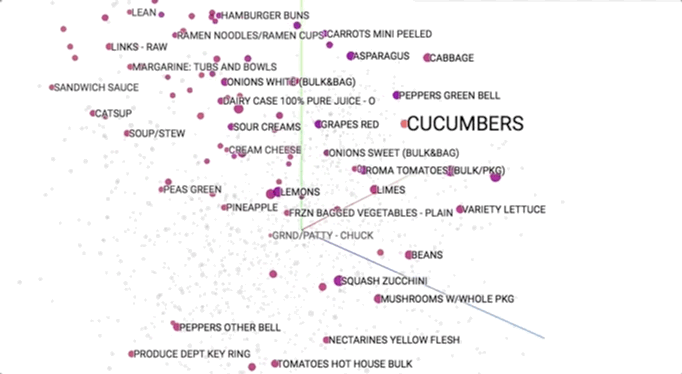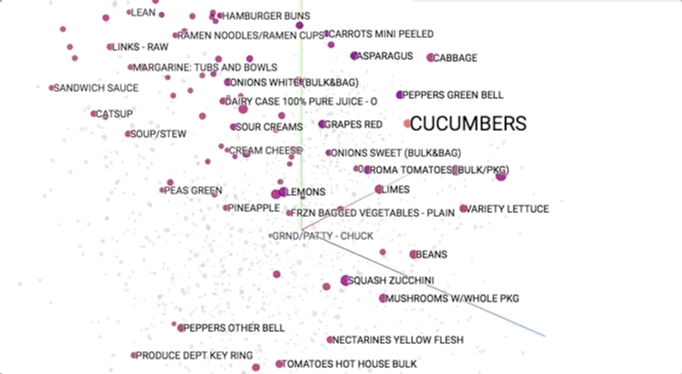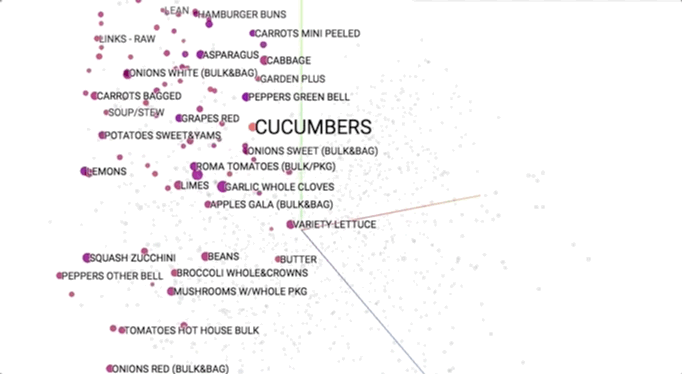
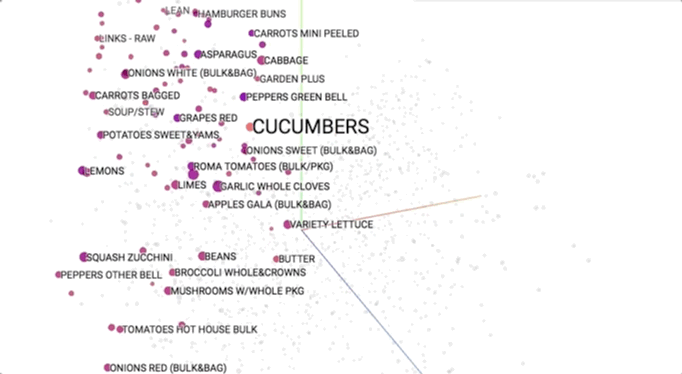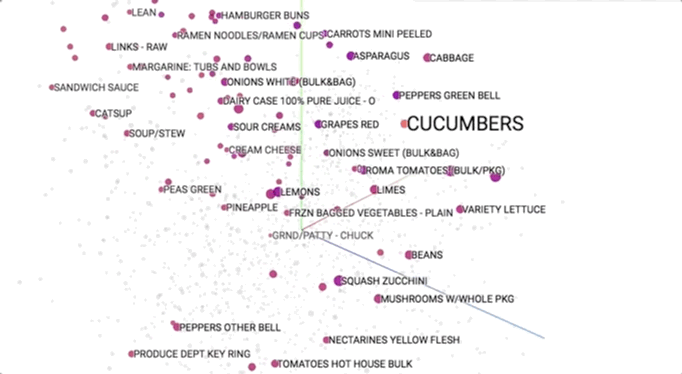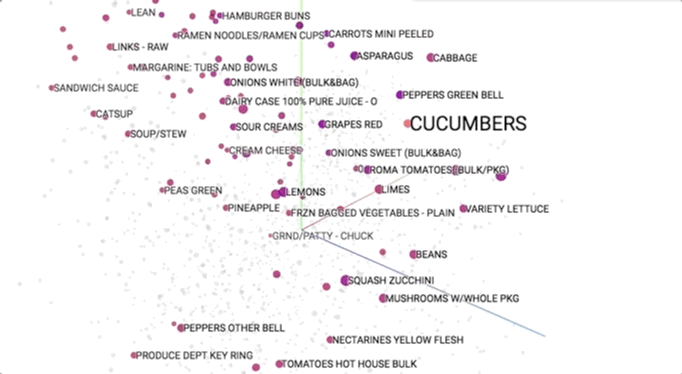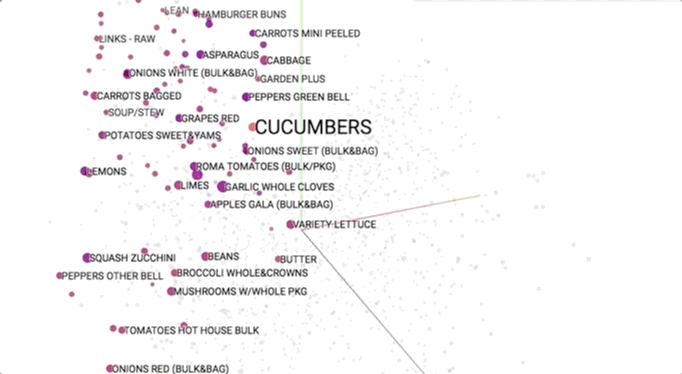
Semantic models is pictured geometrically. Similar merchandise ought to occupy close regions of linguistics house. to be told additional regarding these visualisations, see this speak.
This provides our initial glimpse into however we have a tendency to shoppers be of the overwhelming selection close US. As we have a tendency to expertise merchandise along (e.g., in searching baskets), we have a tendency to use that information to cluster them along into linguistics themes. This helps US to allow structure to Associate in Nursing otherwise discouraging ocean of choices and ultimately impute aiming to them.
Foraging within the mind

When buying groceries on-line, however does one decide what to look for next?
To understand what quantity this linguistics information influences our decisions, we will use models like LDA to predict them.
In experimental tasks, psychologists have measured the influence of LTM by asking folks to list as several things as they will from at intervals a class (known because the linguistics fluency task). Have a go now; attempt to list as several animals as you'll be able to at intervals two minutes employing a pen and paper.
Typically, participants during this task list things consecutive that area unit shut linguistics associates. as an example, they may list cat then dog, then listing all the pets they will consider before transitioning to yard animals. Psychologists have likened this to forage, wherever we have a tendency to take tiny steps around our LTM once looking for the most effective words to retrieve.
The results of our second project (published in Science Advances) showed that these ideas can be extended to clarify however folks write searching lists or hunt for groceries on-line. In theory, we will list things or hunt for groceries on-line in any order. However, our results showed that consecutive purchases cared-for be shut associates in memory. The additional similar 2 merchandise area unit in LTM, the additional doubtless we have a tendency to area unit to buy them in sequence. It’s as if we’re forage around our memory of merchandise once deciding what to shop for next.
In addition to linguistics information, shoppers conjointly recruit reminiscences of previous experiences once looking for groceries (known as episodic memory). as an example, we have a tendency to might bear in mind mistreatment 2 merchandise along in an exceedingly instruction or shopping for them along in previous visits. Our results steered that shoppers United Nations agency relied on this episodic information once they shopped were less doubtless to forget merchandise at the top of their visit. If you’re at risk of forgetting merchandise, attempt prompting yourself to consider alternative merchandise that you’ll want aboard the one you last bought (e.g., shopping for cereal? Get milk!)
Summary
It will generally feel as if there's an excessive amount of selection. I tend to feel this most in domains wherever I actually have the smallest {amount} amount of expertise, like looking for hotels in an exceedingly new town. The analysis mentioned during this article helps US to know why.
As we have a tendency to expertise choices, we have a tendency to develop Associate in Nursing more and more wealthy long information that helps to guide our selections. As mentioned earlier, we have a tendency to naturally begin to section choices into linguistics clusters at intervals our heads, like “stir fry” and “breakfast foods”. Incredibly, this linguistics information is reverse built from shoppers’ decisions. We’re mistreatment this at dunnhumby to raised verify that merchandise area unit substitutable and which enhance one another.
These findings conjointly emphasise the advantages of blending psychological theory and large knowledge analyses. The market may be a nice model for finding out decision-making, partially as a result of there area unit such a large amount of decisions created across such a large amount of choices, and we’re quite sensible at pursuit those decisions over time. Combining work tasks, machine learning and large knowledge will reveal powerful insights regarding the decision-making processes of shoppers and these facilitate retailers to serve customers higher at scale.