Ø Fuel supply system
Ø Transmission System
Ø Suspension Sysytem
Ø Braking System
Ø Steering System
Ø Gasoline Engine
Ø Cooling system
Ø Electrical System
Ø Ignition System
Ø Exhaust System
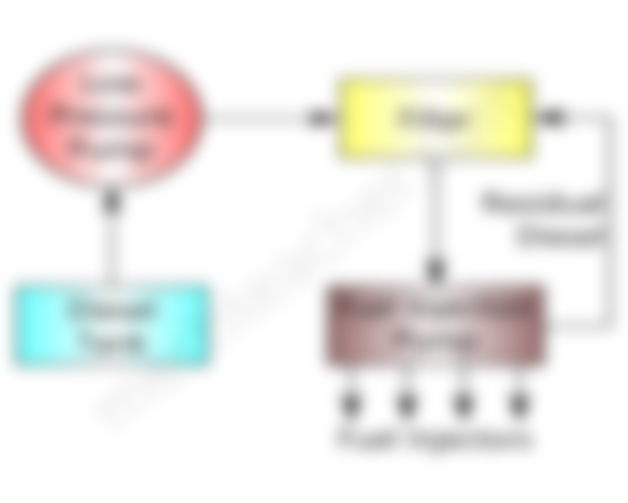
Fuel Supply System:
Fuel supply system is a seperate system used to deliver diesel at correct time in correct quantity, to a diesel engine for smooth and efficient operation.
The operation of a diesel engine is different from that of a petrol engine. In a petrol engine, air-fuel mixture is supplied by a carburetor to the engine, at the beginning of the suction stroke. But in a diesel engine, fuel (without air) is supplied at the end of the compression stroke, by means of a fuel supply system.

Transmission System:
The mechanism that transmits the power developed by the engine of automobile to the engine to the driving wheels is called the transmission system (or power train train).
It is composed of-
Ø Clutch
Ø The gear box
Ø Propeller shaft
Ø Universal joints
Ø Rear axle
Ø Wheel
Ø Tyres

Suspension System:
The Suspension System is designed to provide a smooth ride for you and your passengers and to safely keep all the wheels in contact with the ground at all times, given all road conditions.Technological improvements are constantly being made to optimize the suspension system.
Main components of the Suspension System:
· Tires
· Wheels (rims)
· Shock Absorbers (dampers)
· Springs
· McPherson Strut Suspension
· Upper Control Arms (A-arms)
· Lower Control Arms
· Sway Bars (anti-roll bars)
· Torsion Bars
· Axle System
· Driveshaft
· Wheel Alignment
· Tire Pressure
Braking System:
A brake is a mechanical device which inhibits motion.
Types of Brakes:
Ø Mechanical Brakes
Ø Drum Brakes
Ø Disc Brakes
Ø Hydraulic Brakes
Ø Power Brakes
Ø AIR Brakes
Ø Air Hydraulic Brakes
Ø Vaccum Brakes

Steering System:
The steering system converts the rotation of the steering wheel into a swivelling movement of the road wheels in such a way that the steering-wheel rim turns a long way to move the road wheels a short way.
The system allows a driver to use only light forces to steer a heavy car. The rim of a 15 in. (380 mm) diameter steering wheel moving four turns from full left lock to full right lock travels nearly 16 ft (5 m), while the edge of a road wheel moves a distance of only slightly more than 12 in. (300 mm). If the driver swivelled the road wheel directly, he or she would have to push nearly 16 times as hard.
The steering effort passes to the wheels through a system of pivoted joints. These are designed to allow the wheels to move up and down with the suspension without changing the steering angle. They also ensure that when cornering, the inner front wheel - which has to travel round a tighter curve than the outer one - becomes more sharply angled.
The joints must be adjusted very precisely, and even a little looseness in them makes the steering dangerously sloppy and inaccurate.
There are two steering systems in common use - the rack and pinion and the steering box.On large cars, either system may be power assisted to reduce further the effort needed to move it, especially when the car is moving slowly.

Cooling System:
The purpose of the Engine Cooling System is to prevent the overheating of your vehicle’s engine. With engine combustion reaching extremely high temperatures, the resulting heat needs to be dissipated. An efficient cooling system is essential to prevent the engine from burning!! Another function of the cooling system is to regulate the temperature inside the passenger compartment, insuring your comfort and that of your passengers.
On most recent vehicles, the engine cooling system is pressurized. You should not attempt to effectuate maintenance or repair work on the system. Servicing or repairing this system requires specific tools and adequate training.
Main Components of the Engine Cooling System:
Ø Radiator
Ø Cooling Fluid - Coolant
Ø Radiator Fan
Ø Radiator Hoses
Ø Water Pump
Ø Heater Core
Ø Temperature Knob
Ø Temperature Control Valve
Ø Thermostat
Ø Temperature Gauge
Ø Temperature Sensor
Ø Reservoir or Reserve Tank
Ø Radiator Pressure Cap

Electrical System:
Electrical system consists of the battery, starter and alternator. The battery provides juice to the starter. Then, the alternator gives that battery the energy it needs to power your car. If one of these parts is not working properly, your car won’t start or run correctly.
Battery:
Until your vehicle starts, your battery is providing the car’s entire electrical current. This includes the current to the ignition and fuel systems, which are responsible for creating the combustion necessary for your engine to function.
Starter:
While the battery supplies the power to start your vehicle, the starter is really what gets the engine going. The battery supplies a small amount of power to the starter motor. The starter then rotates the flywheel, which turns the crankshaft and begins the movement of the engine’s pistons. This intricate process is why it’s key to make sure the starter works.
It’s difficult to determine when a starter will fail exactly, but an electrical system check at Firestone Complete Auto Care can help recognize the warning signs. We check if the starter is drawing the proper amount of current. An excessive current draw will indicate a worn starter, while a low current draw points to corroded cables or connections.
Alternator:
When your engine is running, the alternator keeps the battery charged and the electrical system going. Your car can start with a faulty alternator, but it won’t be able to run for an extended period of time. If the alternator requires replacement, your vehicle’s electrical system will perform erratically, its battery will discharge, and eventually your engine will lose power. A complete electrical system check from Firestone Complete Auto Care will tell you whether the alternator is generating the proper amount of current and voltage. That way, you have a heads up before your alternator fails.
Working:
So you turn the key and your vehicle’s electrical system goes into action. The battery provides juice to the starter, the starter turns and the alternator gives the battery the energy it needs to power your lights, defroster, wipers and accessories. See how it works:

Ignition System:
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines oil-fired and gas-firedboilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ignition internal combustion engines is in petrol road vehicles: cars (autos), four-by fours (SUVs), pickups, vans, trucks, and buses.
Working:
Four-stroke engines have used a mechanically timed electrical ignition system. The heart of the system is the distributor. The distributor contains a rotating cam driven by the engine's drive, a set of breaker points, a condenser, a rotor and a distributor cap. External to the distributor is the ignition coil, the spark plugs and wires linking the distributor to the spark plugs and ignition coil. (see diagram Below).
The system is powered by a lead-acid battery, which is charged by the car's electrical system using a dynamo or alternator. The engine operates contact breaker points, which interrupt the current to an induction coil (known as the ignition coil)

Exhaust System:
The exhaust system is an assembly in a vehicle's engine that takes care of the burnt gas that the engine produces.
Construction:
· Header
· Catalytic Converter
· Muffler
· Turbocharger
Working:
The exhaust system is an assembly in a vehicle's engine that takes care of the burnt gas that the engine produces. It consists of exhaust pipes, through which exhaust gas flow through from one chamber to another, a header, which collects the same gas from different cylinders and directs it to the pipes, a catalytic converter, which converts the pollutant gases produced during combustion into less harmful substances, a muffler, which reduces engine noise, and a turbocharger, which increases engine power.
The exhaust system is vital to any vehicle because the life and performance of the vehicle's engine depends on it. An engine cannot function well if there is back pressure trapped in it. Trapped exhaust gas chokes an engine and stops it from doing productive work. As a result, the vehicle cannot run smoothly and silently, or in the worst cases.
This part of the auto framework is so important that some vehicles run on dual exhaust systems. The engines of such vehicles can give off exhaust gas more freely.
Thus, a superior auto exhaust system is necessary for any type of vehicle. The bigger the exhaust pipes of an exhaust system are, the better, because exhaust gas can take their exit more freely that way. The government in most states is not kind to motorists who run on defective exhaust systems, and so utmost care must be taken in purchasing the right exhaust system.