Personally I think that in order to understand this technology, the BITCOIN and cryptocurrency in general, you have to start with the first thing in order to begin to find the fundamentals and the why of things.
In that first publication we had seen that the Blockchain was not born with Bitcon , but that this was the first application on a Blockchain. We had said that the concept of encrypted blockchains already existed but that until before Bitcoin it had not been possible to successfully realize one.
When Satishi Nakamoto sent the email to all his cryptographic contacts sending the Bitcoin white paper, he did it to solve part of the 2008 financial crisis caused by the real estate bubble. Let's remember that Nakamoto's main idea was to devise a cryptographic system that would enable the transfer of value from person to person without the need for financial intermediaries, which would make the system more economical and efficient.

We also saw that Blockchain Technology not only has application in cryptography, but is applicable to multiple areas of our real life, such as voting systems, real estate registration, to determine the traceability of food, keep medical records of people, among others.
It is clear that not all blockchains are secure, immutable, transparent, open to innovation, etc. For this we needed it to be decentralized as this would imply that this blockchain would not be modified by the will of one person or a few.
Decentralization is a key factor in blockchains and is what will provide security and trust in the ecosystem and ensure the safekeeping of the data entered in it.
Later on I will share with you the Bitcoin white paper and we will make a brief analysis of it to finish understanding it.
When we talked about the problems that these types of technologies could present, we referred to centralization, which implies a very big risk, and the other big problem of scalability, which implied that the system became slow when a large number of users were inside the system.
To solve these problems they are working with second layer blockchain such as Polkatot or Cardano, both built on the Etherum blockchain. Later we will see briefly what problems each one came to solve and why both are among the best projects we can find in the world of cryptography.
Now if entering the topic that I want to discuss today we will begin to advance in the topic of blockchain technology applied to cryptocurrencies.
It is necessary to know that each currency has its Blockchain and that in each of them there are different elements that make them more or less decentralized.

Bitcoin in the most decentralized, open, secure and immutable blockchain that exists.
When we want to invest in another currency we should analyze on which blockchain it is programmed, analyze its degree of decentralization, if it presents scalability problems and what is the solution to those problems.
What are the elements that make Bitcoin decentralized:
1 - The Blockchain.
2 - Consensus mechanisms.
3 - The public Cryptografy, or public record cryptography.
4 - Proof of work decentralized algorithm.
These elements make Bitcoin an immutable, secure, transparent and decentralized blockchain.
Bitcoin is an exchange system where each transaction is recorded and verified by thousands of users (miners = nodes) independently, which makes it a secure, economical and efficient system.
The blockchain is made up of thousands of blocks, each of which has particular characteristics and are connected to each other, hence the idea of chain.
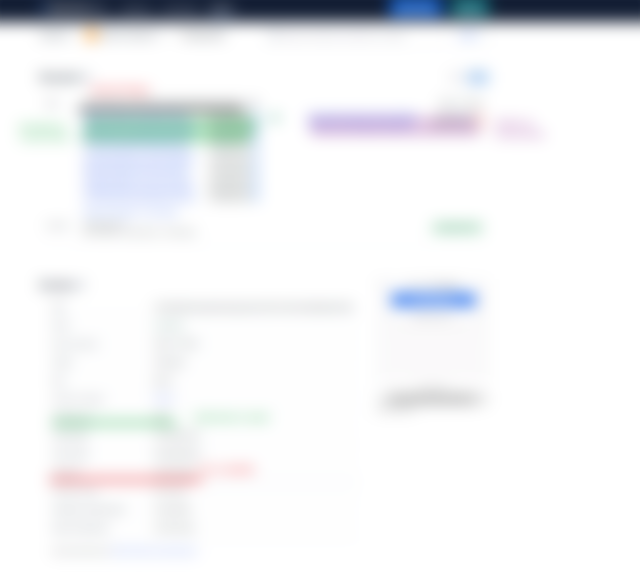
Each block has a number of elements:
- Transaction information; such as the date, the amount, the account from which it is transferred and the account receiving the bitcoin.
Once the information is entered into the block, it cannot be deleted, but only new information can be added, since the blocks are connected to each other by means of cryptographic encryption.
Recall that in the field of cryptocurrencies, the blockchain works as a ledger where all transactions are recorded, which allows the verification of each of them. This provides security and transparency to the exchanges.
- Each block of the chain includes a NONCE (NUMBER THAT CAN BE ONLY USED ONCE) or single-use number.
The NONCE is a unique number that identifies each block and is randomly generated.
- Each block also has a TIMESTAMP. Its purpose is to show the exact time the block was created, validated and stored in the blockchain.
It serves to identify each block on the chain uniquely and without error.
- Each block contains information of the Hash of the previous block.
- It also contains the Hash of that same block.
This is how the chain is formed because as a block has the information of the immediately previous block, all the blocks are linked to the previous block.
If someone tries to modify the information contained in one of the blocks, the structure and the Hash of that block and all subsequent blocks are automatically modified, which invalidates the chain for the other users of the system.
The Timestamp serves to authenticate each block in a unique and individual way so that it cannot be replicated or falsified by system users. The Hash itself and the previous block's Hash are used to bind and is what ensures that it verifies that the information is not altered.
Why does each block have unique elements that differentiate it from other blocks?
The more elements that define the identity of each block, the more difficult it will be to alter the information contained in those blocks.
The alteration of a block implies the alteration of its Hash and the whole structure of the block.
Finally, I will bring you as an example a mined block of the Bitcoin blockchain so that together we can visualize the elements that compose it.
Bitcoin in the most decentralized, open, secure and immutable blockchain that exists.
When we want to invest in another currency we should analyze on which blockchain it is programmed, analyze its degree of decentralization, if it presents scalability problems and what is the solution to those problems.
What are the elements that make Bitcoin decentralized:
1 - The Blockchain.
2 - Consensus mechanisms.
3 - The public Cryptografy, or public record cryptography.
4 - Proof of work decentralized algorithm.
These elements make Bitcoin an immutable, secure, transparent and decentralized blockchain.
Bitcoin is an exchange system where each transaction is recorded and verified by thousands of users (miners = nodes) independently, which makes it a secure, economical and efficient system.
The blockchain is made up of thousands of blocks, each of which has particular characteristics and are connected to each other, hence the idea of chain.
Each block has a number of elements:
- Transaction information; such as the date, the amount, the account from which it is transferred and the account receiving the bitcoin.
Once the information is entered into the block, it cannot be deleted, but only new information can be added, since the blocks are connected to each other by means of cryptographic encryption.
Recall that in the field of cryptocurrencies, the blockchain works as a ledger where all transactions are recorded, which allows the verification of each of them. This provides security and transparency to the exchanges.
- Each block of the chain includes a NONCE (NUMBER THAT CAN BE ONLY USED ONCE) or single-use number.
The NONCE is a unique number that identifies each block and is randomly generated.
- Each block also has a TIMESTAMP. Its purpose is to show the exact time the block was created, validated and stored in the blockchain.
It serves to identify each block on the chain uniquely and without error.
- Each block contains information of the Hash of the previous block.
- It also contains the Hash of that same block.
This is how the chain is formed because as a block has the information of the immediately previous block, all the blocks are linked to the previous block.
If someone tries to modify the information contained in one of the blocks, the structure and the Hash of that block and all subsequent blocks are automatically modified, which invalidates the chain for the other users of the system.
The Timestamp serves to authenticate each block in a unique and individual way so that it cannot be replicated or falsified by system users. The Hash itself and the previous block's Hash are used to bind and is what ensures that it verifies that the information is not altered.
Why does each block have unique elements that differentiate it from other blocks?
The more elements that define the identity of each block, the more difficult it will be to alter the information contained in those blocks.
The alteration of a block implies the alteration of its Hash and the whole structure of the block.
Finally, I will bring you as an example a mined block of the Bitcoin blockchain so that together we can visualize the elements that compose it.
In the coming days I will bring you publications on the "White paper" of Bitconi that Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 to the cryptographic world, where we will clarify several concepts that I mentioned here such as consensus mechanisms and proof of work.
In order to understand and analyze the Bitcoin blockchains and the blockchains of other cryptocurrencies, we must go step by step, slowly but surely.
Little by little I will continue to provide valuable information so that everyone can understand the Blockchain technology, the Bitcoin and the most important blockchains that are called to be the currencies of the future.