Thyroid disease is a type of disease of the endocrine system that affects the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a type of gland located in the neck. It resembles the shape of a butterfly hugging a trachea or windpipe. It produces hormones that help with metabolism, body growth, and sexual development.

If the thyroid gland develops pain, injury, or any kind of problem, thyroid disease can develop. In this condition, the patient may experience various symptoms based on the type of thyroid disease. Often, the patient will experience changes in his or her weight, temperature sensitivity, extreme stress, mood disorders, changes in appearance, and much more.
A person usually develops thyroid disease because it can be swollen or be affected by other conditions. This includes autoimmune disorders. It can also be caused by an improper lifestyle. As a result, the risk of developing thyroid disease is increased due to excessive smoking, not eating foods rich in iodine, and frequent exposure to stress. Apart from these, it can also be inherited, especially if there is a family history of thyroid disease.
In order to treat thyroid disease, it is first necessary to know the cause and type. Depending on the condition, the doctor may prescribe the patient different types of medication or undergo surgery.
History
There has always been a record of the thyroid gland. But then, the only known type of thyroid disease was goiter or goiter. Goiter is a type of thyroid disease in which the patient's neck develops a large tumor due to inflammation of the thyroid.
By 1600 BC, the Chinese were already using seaweed to cure the goiter of patients. By 650 AD, Sun Ssu-Mo used a combination of seaweed, dried shells, and chopped thyroid gland by animals to cure goiter. In 990 AD, Ali-ibn-Abbas was the first to suggest that an operation would cure the patient's goiter.
Although it has long been discovered that seaweed helps a lot to cure goiter, they do not know what it is. But by 1811, Paris discovered that iodine in seaweed was the cause of the goiter.
Apart from goiter, it was also discovered in the 1840s that there were other types of diseases affecting the thyroid gland, such as hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is a type of thyroid disease in which the thyroid gland produces only a few hormones. One of the main remedies for hypothyroidism in 1888 was to give the patient chopped thyroid gland of sheep and currant jelly.
Types
Thyroid disease comes in many forms. Here are the most common types of thyroid disease:
Goiter or goiter. In this condition, the neck develops a large lump due to lack of
Hypothyroidism. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. It may be caused by autoimmune disorders, pregnancy, radiation therapy, and so on.
Hyperthyroidism. This is the opposite of hypothyroidism. In hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland produces excess hormones. It can be caused by tumors in the thyroid or an autoimmune disorder.
Thyroid cancer. In this condition, the thyroid gland develops tumors. It is not fully known why thyroid cancer develops, but it can be inherited.
Causes
There are many different causes of developing thyroid disease. Based on the type of thyroid disease, it can be caused by any of the following:
Having inflammation in the thyroid
Having tumors in the thyroid
Having autoimmune disorders such as Grave’s disease and Hashimoto’s disease
Exposure to too much radioactive iodine
Side effects of radiation therapy on the neck
Changes in hormone levels as a result of pregnancy
Having a thyroid problem from birth
Inheritance of thyroid disease
Smoking
Not eating foods rich in iodine
Frequent stress exposure
Symptoms

Image Source: unsplash.com
When a person develops thyroid disease, he or she may experience various symptoms depending on the type of condition affecting the thyroid gland. Here are some common symptoms a patient may experience:
Weight change. You may experience weight change especially if you have hypothyroidism or With hypothyroidism, you may gain too much weight even if the patient is losing weight. With hyperthyroidism, the patient can lose a lot of weight even if he eats more.
Temperature sensitivity. If thyroid glands produce less hormones, the patient may not suffer from hypothermia. But if too much thyroid gland produces hormones, the patient may feel very hot and sweaty even if the ambient temperature is normal.
Experiencing extreme fatigue and difficulty sleeping. The thyroid gland produces little or no hormones, which patients experience both extreme fatigue and difficulty sleeping.
Having mood disorders. With thyroid disease, the patient may also experience various mood disorders such as depression, anxiety, and anxiety.
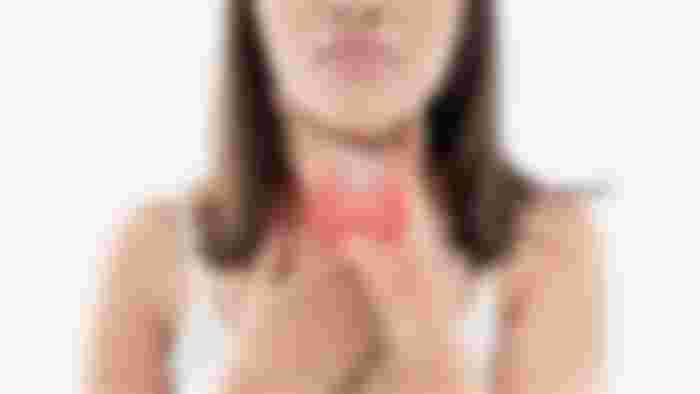
Having neck problems. Because the thyroid gland is located in the neck, there may also be a bad feeling in this part. The patient may experience swelling, difficulty swallowing and breathing, and a rough or screaming voice.
Changes in hair, skin, and nails. Thyroid hormones are also involved in a person's growth and sexual development. Therefore, when the thyroid gland is in trouble, the patient may experience changes in his hair, skin, and nails. If thyroid hormones are deficient, hair can become brittle and brittle, have thick and scaly skin, and brittle and thin nails. If thyroid hormones are high, you may also experience severe hair loss, excessive smooth skin, and strange rashes on the body.
Having constipation problems. If a person has hypothyroidism, he or she may experience frequent constipation. In hypothyroidism, the patient may experience diarrhea.
Having irregular menstruation. Depending on the type of thyroid disease, women may experience strong or weak menstruation. Irregular monthly visits can affect a woman's ability to have children.
Having eye problems. Too many parts of the body are affected by thyroid disease, including the eyes. As a result, the patient may experience dry eyes, blurred vision, teary eyes, and more.
Having trouble with mental activities. The patient may also experience difficulty with mental activities. These include difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, frequent dizziness, confusion, and improper thinking.
Weakness and body aches. In addition to the above, a patient with thyroid disease may also experience weakness and body aches. Parts such as the hands and numbness are also commonly affected
Risk Factors

Image Source: www.futurity.org
Anyone can develop thyroid disease. But the following factors increase the likelihood of developing this condition:
Having a family history of thyroid disease. Children can inherit problem genes from their parents and cause thyroid disease.
Smoking. Cigarettes contain substances that interfere with the absorption of iodine by the thyroid gland. Smoking also causes inflammation in this area.
Frequent exposure to When experiencing stress, the body can produce more hormones to fight this feeling. But it can also have a detrimental effect on the body if overdone.
Obtaining physical damage If the thyroid suffers physical damage, the production of its hormones may be affected.
Using high dosages of some medications. Improper use of drugs such as lithium can affect the thyroid gland and result in thyroid disease. Lithium is commonly used in patients with mood or psychological disorders.
Complications
If thyroid disease cannot be cured, it can result in various complications such as:
Having blurred vision
Heart disease
Broken bones
High blood pressure
Numbness of the body
Infertility
Abortion in the womb
Mental disorder
Myxedema
To avoid
Image Source: www.freepik.com
To prevent the development of any type of thyroid disease, keep the thyroid gland active in the following ways:
Eat enough. Make it a habit to eat a balanced and nutritious diet at the right time to keep healthy parts of the body, such as the thyroid gland. Eating iodine-rich foods such as seaweed and fish is also helpful.
Avoid excessive exercise. Excessive exercise prevents the entry of thyroid hormones into the cells of the body. If thyroid hormones are not used properly, there may still be fat in the waist and abdomen even when exercising.
Stop smoking.
Do not have X-rays if not necessary. Frequent X-rays can cause damage to thyroid gland cells because they contain radioactive elements that are harmful to the body.
Only take the correct dosage of the drug. If you are currently taking medication, make sure its dosage is correct so as not to damage the thyroid gland.
Avoid stress. Stay away from anything or anyone that could cause you stress. If unavoidable, some stress relieving activities such as yoga, meditation, exercise, and so on are helpful.