Cell Structure and Function
The cell is the building block of each living organism. Each cell is a self-contained system that undergoes the functions of energy production and usage, restoration, reproduction, and excretion. Calls join together to form tissues, tissue joins to form organs, and organs form body systems. To understand how the organs and systems of the body work, one must first understand the cell. This understanding requires an investigation of the individual structures that make up the cell and of the separate function each structure carries out to serve the whole.
PHYSIOLOGIC CONCEPTS
Cell Structure
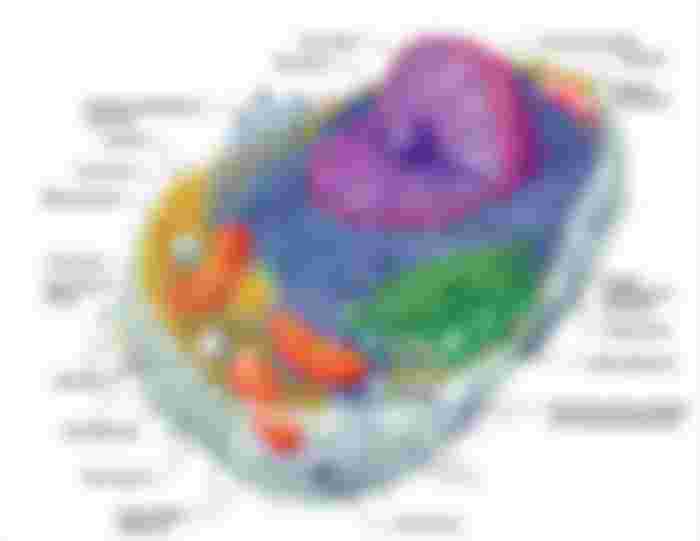
A cell is made up of internal structures separated from each other by semi-permeable membranes. These internal structures are bound together inside one cell membrane to form a single unit. Although cells differ as to their function in the body, all cells contain the same internal structures. The inside of each cell can be divided into two main compartments: the cytoplasm and the nucleus. All internal structures reside in the cytoplasm or the nucleus.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm includes everything inside the cell but outside the nucleus. The mitochondria are the energy sources of the cell, and the endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes are cytoplasmic structures (organelles) necessary for protein synthesis. The Golgi apparatus is a complex of membranes and vesicles responsible for the secretion of proteins synthesized on the ribosomes. Intracellular lysosomes are vesicles that contain potent digestive enzymes. The internal skeleton, called the cytoskeleton, consists of microtubules and microfilaments. The cytoskeleton supports the cell from the inside and allows for the movement of substances inside the cell. The cytoskeleton also supports the movement of projections on the outside of cells, such as the hair-like projections called cilia. The microtubules play an important role in chromosome separation during cell division and assist in maintaining structural integrity.
The Nucleus
The nucleus of the cell is a large, membrane-bound organelle that contains deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the genetic material of the cell. To protect itself from breakage, the DNA is folded up inside the nucleus. Proteins responsible for folding and protecting the DNA are called histones. Histones and DNA are found in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus. DNA replication, cell division, and DNA transcription occur inside the nucleolus.
Cell Membrane
A cell membrane encircles each cell. The cell membrane is a semipermeable barrier, composed of a floating bilayer of phospholipids.
TO BE CONTINUED...