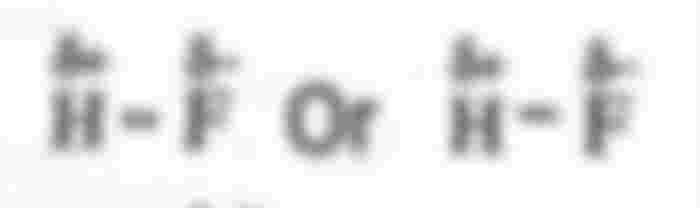One of the user here on read.cash @kingofreview had requested me to write an article on polarity.i am not saying i am an expert.But you can say i know a little about this. As i am going to make an article on it. I hope it will be helpful.
Let's start, with a chart

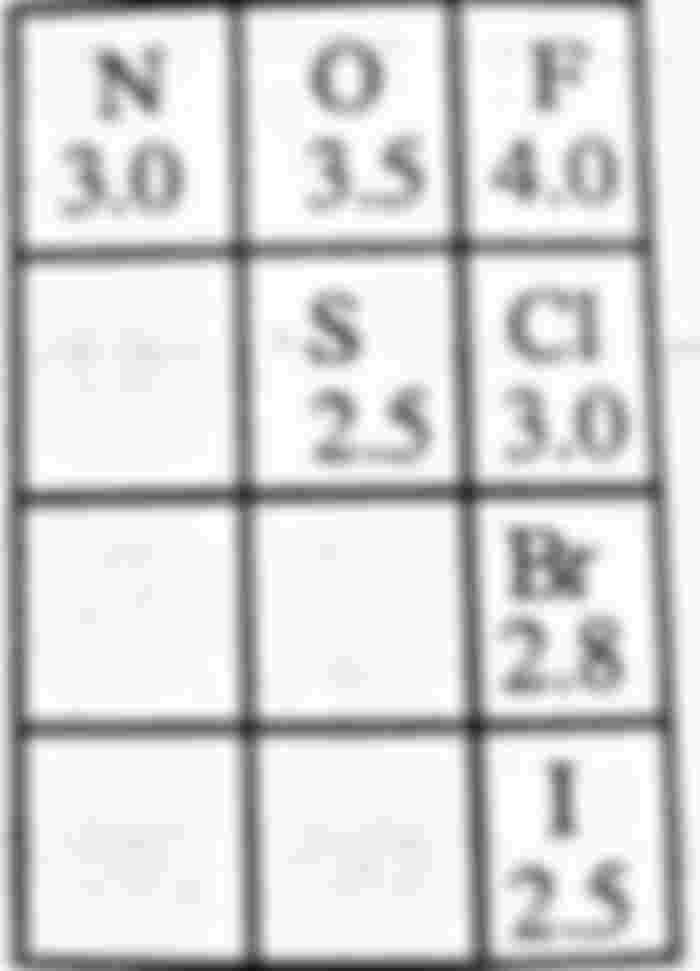
The ability of an atom to attract more of the shared electron pairs of covalent bonds to itself is called the electronegativity of that atom. Non-metals have higher electrical negativity and metals have lower electronegativity. The electronegativity of fluorine is highest, followed by oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen atoms. The denser the shared electron cloud, the more electrons are attracted to the negative atom. The result is a partial negative charge in that atom (6–) and a partial charge in the other atom. Positive charge (+) is generated.E.g

According to the Pauling scale, the values of electronegativity of some elements are F = 4, 0 = 3.5, C1 = 3.0, N = 3.0. Br = 2.8, I = 2.5, C = 2.5 H = 2.1
What is dipol and polarity
Dipole and Polarity: Due to greater difference in electronegativity of the two atoms of the covalent compound (Usually between 0.5–1.9) Two different charges or poles are formed at the two ends of the molecule, both poles together are called dipole. The nature of the formation of a dipole in a molecule of a covalent compound is called the polarity of that compound. Because two different poles are formed at the two ends of a molecule, that molecule is called a polar molecule or a polar compound. HE, H2O are polar compounds.
Example,
HF is a maximum polar molecule; Because of the difference in electronegativity of F and H atoms (4–2.1) = 1.9 by which The highest polarity is expressed among the polar molecules. Of the halogens, F is the most electrically negative HF Most polar molecules. The polar orientation sequence of hydrogen halide molecules is HF> HCI> HBr> HI; In essence The greater the difference in the negativity of the bound atoms, the greater the ionic properties of the compound.
Good to know
In reality there is no 100% ionic compound. Similarly 100% covalent compounds (No) in NaCl compound approx Has 80% ionic properties. The following table shows the difference between the electronegativity of atoms and the compounds formed by them The average percentage of features is shown.E.g


Due to the formation of partial positive and negative electric charges in covalent molecules, the properties of partial ionic compounds are revealed in those compounds. A new intermolecular force called hydrogen bonding is formed between H-atomic polar molecules. The molecules of all these compounds are associated. H-bonding causes differences in compounds.
For example,
in all compounds, the properties of partial ionic compounds are seen in the form of physical state, melting point, density, etc. The hydrides of oxygen and sulfur in group 16 (6A) are H2O and H2S, respectively. In this case HO is liquid, but Opolar H2S is gas.Acid molecules like HCL, H2SO4, HNO3 etc. are polar. They give H + ions in water, expressing acidity. Like the aqueous solution of NaCl, the aqueous solution of all these acids is electrically conductive. The reaction of ionic compounds in aqueous solutions occurs very quickly. Similarly, these polar covalent compounds react rapidly when dissolved in water. The reaction in pure covalent compounds is slower than the reaction in ionic compounds.
Polarisation of Ions
When a cation comes very close to an anion, the nucleus of the cation, that is, the total positive charge, attracts the electron cloud of the anion to itself. At the same time the cation repels the nucleus of the anion. As a result of this attraction and repulsion, the electrons of the anion move towards the cloud cation. This is called deformation or polarization of anion by cation. The anion is then said to have been polarized by cation.

The state of the two ions in the full ionic bond, the distortion of the electron cloud in the anion as a result of polarization, the state of the electron cloud in the polar covalent bond and the pure covalent bond are illustrated by the following figure:

So make it simple, if you think the hard way,it will be difficult for you. First, think as you can do everything and then try hard.nothing comes by own, you have to bring it by working hard.
If you want to learn about bonds then here is one in youtube
Chemistry is really an easy subject if you understand the matters of it then.if you don't understand then try to understand and really try hard otherwise you won't be familiar with chemistry. I hope chemistry will bring light in your life.
More chemistry based articles are yet to come till then, stay happy, eat well, be health, always keep smiling.
Sources
Lead image source - https://unsplash.com/photos/8UXIh-pc9YA
Other images are screen shots and edited by me

If you want to join me on noise.cash then feel free to visit https://noise.cash/u/Laurenexai