Ethereum 2 (ETH2 or ETH 2.0 or ‘Serenity’) is a set of upgrades that improve the scalability, security, and sustainability of Ethereum. Although each is being worked on in parallel, they have certain dependencies that determine when they will be deployed. ETH 2.0 embodies improvements put in place to increase the productivity of the pioneering Ethereum blockchain network. ETH 2.0’s primary goal is to ensure efficiency and implementation of the smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
The new version of Ethereum will be launched in several phases. Each of these phases will include a new and improved feature for the blockchain and boost the network’s efficiency.
The expected initial phase of this upgrade began late 2020. The initial step will be regarded as Phase 0 and will slowly advance until it reaches the final phase.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
The purpose of this upgrade is to change the system currently being used, which is a Proof of Work
(PoW) chain as adopted by many blockchains. This also falls in line with several pre-planned updates to the network since its launch back in 2015.
The new updates on Ethereum 2.0 will solve problems associated with scaling, mining, high gas fees, and security, among others. The upgrade will offer several solutions such as faster transactions and a way to effectively operate decentralized (dApps) and Proof of Stake.
Difference Between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0
There are several distinct features between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0. The differences can be found in specific upgrades present in Ethereum 2.0 but not in the former. These updates are known as Proof of Stake (PoS) and Shard Chains.
Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake is an upgrade to the Proof of Work used on Ethereum 1.0, which expends computing power and electricity to increase the blocks on a blockchain. This Proof of Stake can be easily implemented without excessive power consumption and will provide increased security. Instead of relying on extreme power to operate, it uses stakes and validators.
Shard Chains
Shard chains can be described as procedures that enhance the network’s quality and was released with the launch of Ethereum 2.0.
Currently, a chain comprises a series of blocks. This is to ensure that the network is secure and to verify the information quickly. The downside to this is that transaction speed may slow down when numerous transactions coincide.
Shard chains, however, solve this lagging problem by providing a means to divide the blockchain to allow data to be processed by several nodes instead of a full node verifying each transaction on Ethereum 1.0.
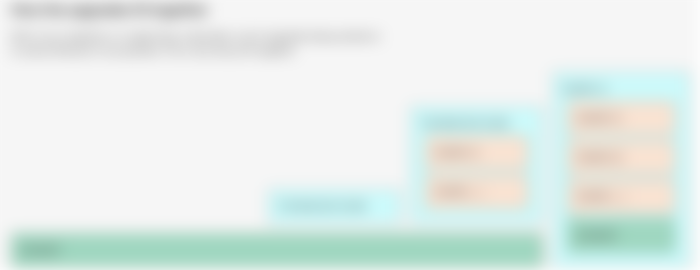
Ethereum 2.0 Roadmap
The launch of Ethereum 2.0 has been divided into three different phases to ensure a smooth transition ultimately. Below is a brief outlay of the three steps
Phase 0: This is the first step for the upgrade and was initiated in 2020. This introduced the Beacon Chain, which will bring forth Proof of Stake. The Beacon Chain will help manage validators who are meant to verify blocks. The Beacon Chain is the first Eth2 addition to the ecosystem. It brings staking to Ethereum, lays the groundwork for future upgrades, and will eventually coordinate the new system. The Beacon Chain is currently live.
Phase 1: The launch of Phase 1 is still undetermined, but it is expected to launch sequentially after the Beacon Chain. This phase will showcase Shard chains, which is to enhance productivity on the network. Shard chains will expand Ethereum’s capacity to process transactions and store data. The shards themselves will gain more features over time, rolled out in multiple phases.
Phase 1.5: This phase sees a merger between new and existing blockchain to develop one Ethereum network. In other words, it can be described as merging the PoW with the PoS chain. Mainnet Ethereum will need to “dock” or “merge” with the Beacon Chain at some point. This will enable staking for the entire network and signal the end of energy-intensive mining.

Phase 2: The period when this would be launched is still unknown but should see deposits, transfers, implementation of smart contracts, etc.
After Phase 2: Consistent updates and modifications would happen on the blockchain after phase 2 has been completed. It could also see new features added to the blockchain.
Ethereum 1.x: This phase is designed to keep Ethereum 1.0 functioning until step 1 of the second version has been completed.
Staking on Ethereum 2.0
A minimum of 32 ETH is needed to have been traded by validators before verifying exchanges on Ethereum 2.0. Also, this minimum stake is placed in a deposit contract in the Ether ecosystem. Furthermore, client software is needed to be able to verify blockchain transactions. The validators, in turn, earn rewards for the transactions they have confirmed.
Conclusion
Ethereum 2.0 brings a lot of promises to eliminate all the problems of Ethereum 1.0. The Proof of Stake, which will replace PoW, is determined to reduce mining expenses and the possibility of fraudulent operations on the network. There looks to be a possible merger for both blockchains to become a single unit in the coming years. This is to allow for seamless operation on the network.
Originally posted on https://decentralised.africa/