Antimicrobial Resistance Awareness week; general information regarding AMR
Every year 18 November to 24 November is celebrated as Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) awarness week throughout the world. This is a relatively new topic but the debate is going on for the past 2 years. Scientists and medical communities are more concerned about the alarming rate of the spread of antimicrobial resistance. A report has shown the death rate due to antibiotic resistance is quite more than that of HIV and other infectious diseases.
Introduction to Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR);
AMR refers to a certain condition, in which different microorganisms stop responding to those that are drugs used to treat them. Therefore making the infection worst which can result in acute and chronic disease.
When the microorganisms develop resistance against the drug, it becomes difficult to treat them. The resistance may develop due to mutations in their genetic material and modification in proteins that are the spots for Antibiotics.
Common AMR containing microorganisms;
The microorganisms included in this catagory can be bacteria, viruses, or fungi. .
The common genera of bacteria carrying resistance genes in them include Ochrobactrum, psedumonella, serratia, Burkholderia, etc...
Reasons for AMR spread;
There are numerous reasons behind the spread of AMR spread, It can spread naturally.It can also spread due to the extensive use of antibiotics. Another major reason is the poor hygienic conditions.
How to Check if an organism is carrying resistance to certain antibiotics;
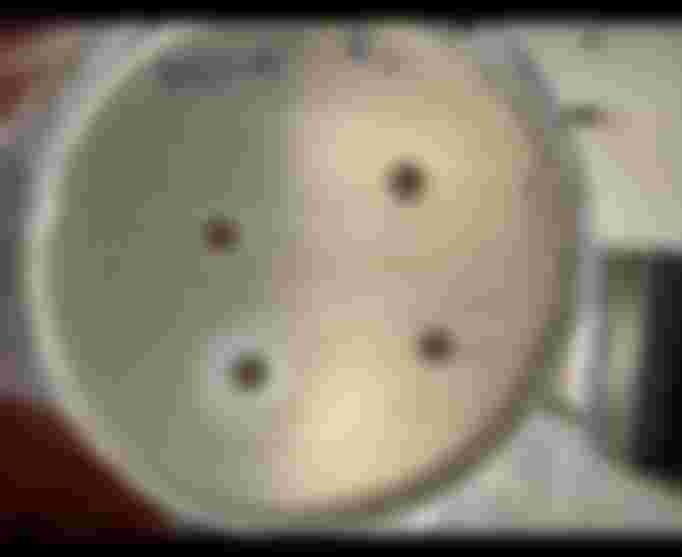
To date, the most common method utilized in this regard is the Kirby bauer disk diffusion method. It is known as the best technique utilized for this purpose.
In this method first, we prepare a freshly grown inoculum of microorganisms. Then we spread the culture with the help of sterilized cotton bud on a Perti dish containing particular growth media. Then we put the discs of antibiotics against which we want to check resistance. A sterilized syringe is required for putting discs and all the procedures require extreme caution and can be done only inside Laminar Flow Hood.
Afterwards, we keep the plated dishes in an incubator by setting the desired temperature. The next day we measure the zones of inhibition (circles around antibiotics) and then compare them with standardized zone points. This gives the idea of whether that particular microorganism is resistant to used antibiotics or not.

I did extensive research on this topic in my MS research. I am ending this topic here because my paper is in process of publication. I am not allowed to reveal information till my paper got published. I hope I provide enough knowledge about antibiotic resistance microorganisms spread.
(Disclaimer! I covered this topic based on the knowledge I acquired during my education time. This article belongs to me and is free of plagiarism. However, the specific methods, general names, etc are available in the literature as it is scientific information).
Images included in this article are taken by me during research.
What a informative and interesting contents. Nicely explained and detailed article